Page 66 - Libro 2
P. 66
46
PART 2 — CEREBROVASCULAR
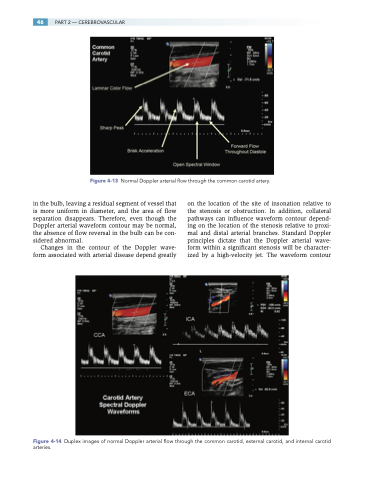
Figure 4-13 Normal Doppler arterial flow through the common carotid artery.
in the bulb, leaving a residual segment of vessel that is more uniform in diameter, and the area of flow separation disappears. Therefore, even though the Doppler arterial waveform contour may be normal, the absence of flow reversal in the bulb can be con- sidered abnormal.
Changes in the contour of the Doppler wave- form associated with arterial disease depend greatly
on the location of the site of insonation relative to the stenosis or obstruction. In addition, collateral pathways can influence waveform contour depend- ing on the location of the stenosis relative to proxi- mal and distal arterial branches. Standard Doppler principles dictate that the Doppler arterial wave- form within a significant stenosis will be character- ized by a high-velocity jet. The waveform contour
Figure 4-14 Duplex images of normal Doppler arterial flow through the common carotid, external carotid, and internal carotid arteries.