Page 175 - Libro vascular I
P. 175
Chap-12.qxd 29~8~04 14:52 Page 166
166
PERIPHERAL VASCULAR ULTRASOUND
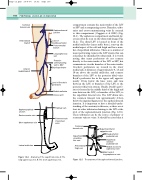
compartment contains the main trunks of the LSV or SSV and accompanying nerves. Branches, tribu- taries and cross-communicating veins lie external to this compartment (Caggiati et al 2002) (Fig. 12.1). The saphenous compartment and fascial lay- ers can often be seen on the ultrasound image (Fig. 12.2). The distal LSV is located in front of the medial malleolus (inner ankle bone), runs up the medial aspect of the calf and thigh and has a num- ber of superficial tributaries. There are a number of major perforating veins in the LSV system that can sometimes be identified by ultrasound. It is worth noting that many perforators do not connect directly to the main trunks of the LSV or SSV, but communicate via side branches of the main trunks. Crocket’s perforators are located in the lower medial calf, at distances of approximately 6, 13 and 18cm above the medial malleolus, and connect branches of the LSV to the posterior tibial veins. Boyd’s perforator lies in the upper calf, approxi- mately 10cm below the knee joint, and runs between the LSV, or branches of the LSV, to the posterior tibial vein system. Finally, Dodd’s perfo- rator is located in the middle third of the thigh and runs between the LSV, or branches of the LSV, to the superficial femoral vein. The LSV drains into the common femoral vein approximately 2.5cm below the inguinal ligament at the saphenofemoral junction. It is important to have a detailed under- standing of the anatomy in this area, as there are at least six other tributaries draining to the LSV at the level of the saphenofemoral junction (Fig. 12.5). These tributaries can be the source of primary or recurrent varicose veins. It should be noted that it
Common femoral vein
Anterolateral branch
Anterior medial branch
Saphenofemoral junction
Level of
Dodd’s perforator
Posteromedial branch
Long saphenous vein
Posterior communicating vein to SSV
Boyd’s perforator
Level of Crocket’s perforators
Medial malleolus Venous arch
Popliteal vein
Common trunk of peroneal veins
Saphenopopliteal junction
Gastrocnemius vein
Short saphenous vein
Lateral malleolus
Common femoral vein
Superficial circumflex iliac vein
Anterolateral thigh vein
Anatomy of the superficial veins. A: The long saphenous vein. B: The short saphenous vein.
Superficial inferior epigastric vein
Deep external pudendal vein
Superficial external pudendal vein
Medial accessory saphenous vein
Main trunk of
long saphenous vein
The anatomy of the saphenofemoral junction.
Figure 12.4
Figure 12.5