Page 184 - Libro vascular I
P. 184
Chap-12.qxd 29~8~04 14:52 Page 175
ANATOMY OF THE LOWER LIMB VENOUS SYSTEM AND ASSESSMENT OF VENOUS INSUFFICIENCY
175
R AB
R
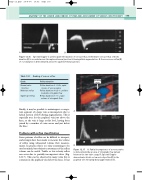
Figure 12.16 Spectral Doppler is used to grade the duration of venous reflux. A: Moderate venous reflux of 0.55 s duration (R) is recorded across the saphenofemoral junction following distal augmentation. B: Severe venous reflux (R) of 2 s duration is demonstrated across the saphenofemoral junction.
Table 12.1 Grade
Normal valve function
Moderate reflux Significant reflux
Grading of venous reflux
Reflux duration
Reflux duration of 0.5 s, rapid closure of venous valves
Reflux duration of 0.5–1 s, mild to moderate retrograde flow
Reflux duration of 1 s, large volume of retrograde flow
Leaking valve
Finally, it may be possible to misinterpret a compe- tent segment of a large vein as incompetent due to helical motion of flow during augmentation. This is especially true for the popliteal vein just above the knee, as the vein is large at this level, having been joined by a number of veins across and just below the knee.
Problems with reflux classification
Some patterns of reflux can be difficult to interpret, and attempts have been made to measure the volume of reflux using ultrasound volume flow measure- ments. In practice this is too time-consuming to be used routinely, but subjective assessment of the reflux volume can be useful. Trickle or low-velocity reflux can occur due to partially incompetent valves (Fig. 12.17). This can be observed in many veins but is common in the popliteal vein below the knee. It has
A
R
A: Partial incompetence of a venous valve is demonstrated by an area of retrograde flow (arrow)
S B
between the two valve cusps. B: Spectral Doppler demonstrates trickle or low-velocity reflux (R) in the popliteal vein following distal augmentation (S).
Figure 12.17