Page 188 - Libro vascular I
P. 188
Chap-12.qxd 29~8~04 14:52 Page 179
ANATOMY OF THE LOWER LIMB VENOUS SYSTEM AND ASSESSMENT OF VENOUS INSUFFICIENCY
179
LSV
Popliteal vein
LSV
SSV
PB
LSV
AB
SSV
GV
GV
SSV MB
PV
PA
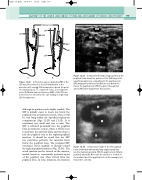
Figure 12.22 A: Posterior varicose branches (PB) of the LSV may interconnect to the SSV distribution in the posterior calf, causing SSV incompetence below the point of communication. (↑, competent veins; ↓, incompetent veins.) B: Medial varicose branches (MB) of the SSV can interconnect to the LSV in the calf, leading to segmental LSV incompetence.
although its position can be highly variable. The SSV is initially easier to locate just below the popliteal fossa in transverse section, where it will be seen lying within the superficial saphenous compartment (Figs 12.2B and 12.23). It is sometimes very small and easy to miss. The SSV is followed proximally into the popliteal fossa in transverse section, where it will be seen to perforate the muscular fascia and run deep to join the popliteal vein at the saphenopopliteal junction. It should be noted that the SSV can sometimes perforate the muscular fascia below the popliteal fossa. The proximal SSV sometimes curves medially or laterally toward the saphenopopliteal junction (Fig. 12.24). The actual junction can be located on the anterior, medial, lateral or, occasionally, posterior aspect of the popliteal vein when viewed from the popliteal fossa. In some situations, the junction
A
A transverse B-mode image just below the popliteal fossa shows the position of the SSV lying in the
superficial, saphenous compartment. The popliteal vein (PV) and gastrocnemius veins (GV) are seen below the fascia. The popliteal vein (PV) lies above the popliteal artery (PA) when imaged from this position.
S
V
Figure 12.23
A transverse image of the left popliteal fossa showing an abnormally large saphenopopliteal
junction (arrow), proximal SSV (S), popliteal vein (V) and popliteal artery (A). Note that the junction is located to the medial side of the popliteal vein in this example, but its position can vary.
Figure 12.24