Page 187 - Libro vascular I
P. 187
Chap-12.qxd 29~8~04 14:52 Page 178
178
PERIPHERAL VASCULAR ULTRASOUND
incompetence of side branches that supply super- ficial varicose areas in the thigh or calf. Another occasional finding is incompetence of the proxi- mal LSV to the level of an incompetent superficial anterior or posterior thigh branch. Beyond the incompetent branch, it is possible for the main trunk of the LSV to be competent.
4. The SFV and proximal popliteal vein above the knee should be assessed for patency and competency. They are imaged from a medial thigh position in longitudinal section. The superficial femoral and popliteal veins lie deep to their respective arteries when imaged from this position.
5. The LSV is then followed in transverse section across the knee along the medial aspect of the calf to ankle. It is common to see large branches dividing from the main trunk of the LSV in the calf. Posteromedial varicose branches of the LSV in the upper calf sometimes interconnect to the SSV system in the posterior calf, causing SSV incompetence below this level (Fig. 12.22). The LSV and its major branches are then assessed in a longitudinal section using distal compression to augment flow. However, the varicose veins may be so obvious in the calf that little time need be spent on assessing the LSV at this level if it is the supply to the varicose areas. The LSV can also supply varicose areas on the lateral aspect of the calf, via incompetent branches that run over the front of the shin. There is considerable debate about the need to examine all calf perfo- rators by duplex, and whether this is done may depend upon local protocols. In many cases per- forators connect to side branches of the LSV and not to the main trunk.
6. The popliteal vein above and below the knee is examined from the popliteal fossa and assessed for patency and competency. The popliteal vein lies superficial to the popliteal artery when imaged from the popliteal fossa. Some clinicians request an assessment of the gastrocnemius veins. The investigation then continues with an assessment of the SSV.
Assessment of the SSV
1. The saphenopopliteal junction is usually located just above the skin crease in the popliteal fossa,
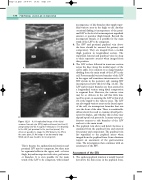
S
J
CFV
A
B
A: A longitudinal image of the distal common femoral vein (CFV), saphenofemoral junction (J)
and proximal LSV (S). A superior tributary is seen draining to the LSV, just proximal to the junction (arrow). It is often not possible to image the CFV distal to the SFJ in the same plane. B: An image of an abnormally large SFJ(J), which was found to be incompetent.
This is because the saphenofemoral junction and proximal LSV may be competent, but there may be segmental reflux in the upper, mid- or lower thigh, beyond incompetent valve sites, perforators or branches. It is even possible for the main trunk of the LSV to be competent, with isolated
Figure 12.21
J