Page 150 - Medical Parasitology_ A Textbook ( PDFDrive )
P. 150
Liver Flukes 143
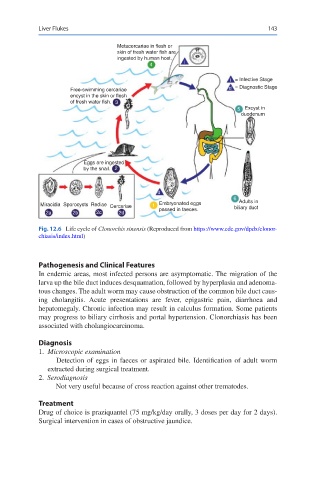
Metacercariae in flesh or
skin of fresh water fish are
ingested by human host.
4 i
i = Infective Stage
Free-swimming cercariae d = Diagnostic Stage
encyst in the skin or flesh
of fresh water fish. 3
5 Excyst in
duodenum
Eggs are ingested
by the snail. 2
d
6
Adults in
Miracidia Sporocysts Rediae Cercariae 1 Embryonated eggs biliary duct
2a 2b 2c 2d passed in faeces.
Fig. 12.6 Life cycle of Clonorchis sinensis (Reproduced from https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/clonor-
chiasis/index.html)
Pathogenesis and Clinical Features
In endemic areas, most infected persons are asymptomatic. The migration of the
larva up the bile duct induces desquamation, followed by hyperplasia and adenoma-
tous changes. The adult worm may cause obstruction of the common bile duct caus-
ing cholangitis. Acute presentations are fever, epigastric pain, diarrhoea and
hepatomegaly. Chronic infection may result in calculus formation. Some patients
may progress to biliary cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Clonorchiasis has been
associated with cholangiocarcinoma.
Diagnosis
1. Microscopic examination
Detection of eggs in faeces or aspirated bile. Identification of adult worm
extracted during surgical treatment.
2. Serodiagnosis
Not very useful because of cross reaction against other trematodes.
Treatment
Drug of choice is praziquantel (75 mg/kg/day orally, 3 doses per day for 2 days).
Surgical intervention in cases of obstructive jaundice.