Page 111 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 111
CHAPTER 6 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology 97
OH
H C O
HO C C α NH 2
H H
Tyrosine L-Amino acid
decarboxylase
Metyrosine – Tyrosine hydroxylase
OH
HO
H C O H H
HO C C NH 2 HO C C NH 2
H H H H
Dopa Tyramine
– COOH Dopa decarboxylase
Dopamine
HO β-hydroxylase
H H
H
HO C C NH 2
O H
H H
Dopamine HO C C NH 2
Dopamine β-hydroxylase H H
Octopamine
HO H Hydroxylase
O H (from liver)
HO C C NH 2
H H
Norepinephrine
Phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase
HO H
O H CH 3
HO C C NH
H H
Epinephrine
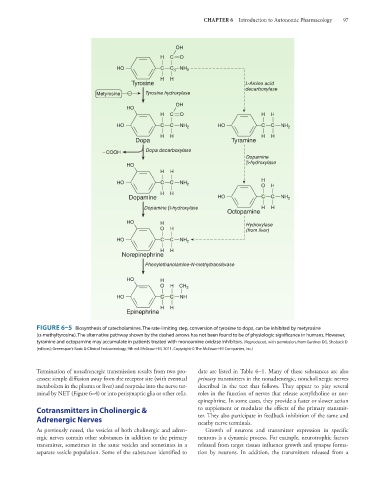
FIGURE 6–5 Biosynthesis of catecholamines. The rate-limiting step, conversion of tyrosine to dopa, can be inhibited by metyrosine
(α-methyltyrosine). The alternative pathway shown by the dashed arrows has not been found to be of physiologic significance in humans. However,
tyramine and octopamine may accumulate in patients treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. (Reproduced, with permission, from Gardner DG, Shoback D
[editors]: Greenspan’s Basic & Clinical Endocrinology, 9th ed. McGraw-Hill, 2011. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.)
Termination of noradrenergic transmission results from two pro- date are listed in Table 6–1. Many of these substances are also
cesses: simple diffusion away from the receptor site (with eventual primary transmitters in the nonadrenergic, noncholinergic nerves
metabolism in the plasma or liver) and reuptake into the nerve ter- described in the text that follows. They appear to play several
minal by NET (Figure 6–4) or into perisynaptic glia or other cells. roles in the function of nerves that release acetylcholine or nor-
epinephrine. In some cases, they provide a faster or slower action
Cotransmitters in Cholinergic & to supplement or modulate the effects of the primary transmit-
Adrenergic Nerves ter. They also participate in feedback inhibition of the same and
nearby nerve terminals.
As previously noted, the vesicles of both cholinergic and adren- Growth of neurons and transmitter expression in specific
ergic nerves contain other substances in addition to the primary neurons is a dynamic process. For example, neurotrophic factors
transmitter, sometimes in the same vesicles and sometimes in a released from target tissues influence growth and synapse forma-
separate vesicle population. Some of the substances identified to tion by neurons. In addition, the transmitters released from a