Page 113 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 113
CHAPTER 6 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology 99
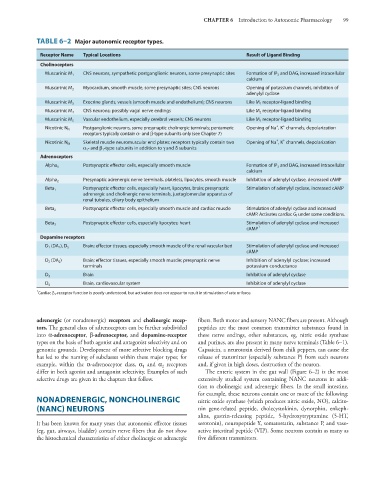
TABLE 6–2 Major autonomic receptor types.
Receptor Name Typical Locations Result of Ligand Binding
Cholinoceptors
CNS neurons, sympathetic postganglionic neurons, some presynaptic sites Formation of IP 3 and DAG, increased intracellular
Muscarinic M 1
calcium
Muscarinic M 2 Myocardium, smooth muscle, some presynaptic sites; CNS neurons Opening of potassium channels, inhibition of
adenylyl cyclase
Exocrine glands, vessels (smooth muscle and endothelium); CNS neurons Like M 1 receptor-ligand binding
Muscarinic M 3
CNS neurons; possibly vagal nerve endings Like M 2 receptor-ligand binding
Muscarinic M 4
Vascular endothelium, especially cerebral vessels; CNS neurons Like M 1 receptor-ligand binding
Muscarinic M 5
+
+
Postganglionic neurons, some presynaptic cholinergic terminals; pentameric Opening of Na , K channels, depolarization
Nicotinic N N
receptors typically contain α- and β-type subunits only (see Chapter 7)
+
+
Skeletal muscle neuromuscular end plates; receptors typically contain two Opening of Na , K channels, depolarization
Nicotinic N M
α 1 - and β 1 -type subunits in addition to γ and δ subunits
Adrenoceptors
Postsynaptic effector cells, especially smooth muscle Formation of IP 3 and DAG, increased intracellular
Alpha 1
calcium
Alpha 2 Presynaptic adrenergic nerve terminals, platelets, lipocytes, smooth muscle Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase, decreased cAMP
Beta 1 Postsynaptic effector cells, especially heart, lipocytes, brain; presynaptic Stimulation of adenylyl cyclase, increased cAMP
adrenergic and cholinergic nerve terminals, juxtaglomerular apparatus of
renal tubules, ciliary body epithelium
Postsynaptic effector cells, especially smooth muscle and cardiac muscle Stimulation of adenylyl cyclase and increased
Beta 2
cAMP. Activates cardiac G i under some conditions.
Postsynaptic effector cells, especially lipocytes; heart Stimulation of adenylyl cyclase and increased
Beta 3
cAMP 1
Dopamine receptors
D 1 (DA 1 ), D 5 Brain; effector tissues, especially smooth muscle of the renal vascular bed Stimulation of adenylyl cyclase and increased
cAMP
D 2 (DA 2 ) Brain; effector tissues, especially smooth muscle; presynaptic nerve Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase; increased
terminals potassium conductance
Brain Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase
D 3
Brain, cardiovascular system Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase
D 4
1
Cardiac β 3 -receptor function is poorly understood, but activation does not appear to result in stimulation of rate or force.
adrenergic (or noradrenergic) receptors and cholinergic recep- fibers. Both motor and sensory NANC fibers are present. Although
tors. The general class of adrenoceptors can be further subdivided peptides are the most common transmitter substances found in
into α-adrenoceptor, β-adrenoceptor, and dopamine-receptor these nerve endings, other substances, eg, nitric oxide synthase
types on the basis of both agonist and antagonist selectivity and on and purines, are also present in many nerve terminals (Table 6–1).
genomic grounds. Development of more selective blocking drugs Capsaicin, a neurotoxin derived from chili peppers, can cause the
has led to the naming of subclasses within these major types; for release of transmitter (especially substance P) from such neurons
example, within the α-adrenoceptor class, α and α receptors and, if given in high doses, destruction of the neuron.
1
2
differ in both agonist and antagonist selectivity. Examples of such The enteric system in the gut wall (Figure 6–2) is the most
selective drugs are given in the chapters that follow. extensively studied system containing NANC neurons in addi-
tion to cholinergic and adrenergic fibers. In the small intestine,
for example, these neurons contain one or more of the following:
NONADRENERGIC, NONCHOLINERGIC nitric oxide synthase (which produces nitric oxide, NO), calcito-
(NANC) NEURONS nin gene-related peptide, cholecystokinin, dynorphin, enkeph-
alins, gastrin-releasing peptide, 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT,
It has been known for many years that autonomic effector tissues serotonin), neuropeptide Y, somatostatin, substance P, and vaso-
(eg, gut, airways, bladder) contain nerve fibers that do not show active intestinal peptide (VIP). Some neurons contain as many as
the histochemical characteristics of either cholinergic or adrenergic five different transmitters.