Page 118 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 118
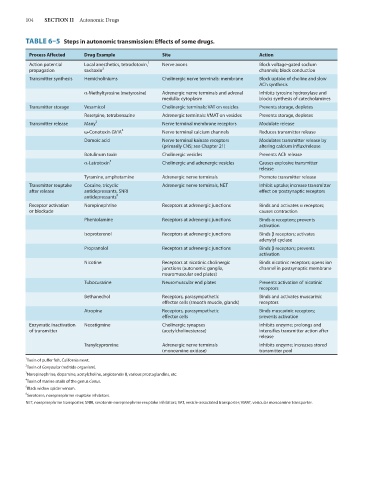
104 SECTION II Autonomic Drugs
TABLE 6–5 Steps in autonomic transmission: Effects of some drugs.
Process Affected Drug Example Site Action
1
Action potential Local anesthetics, tetrodotoxin, Nerve axons Block voltage-gated sodium
propagation saxitoxin 2 channels; block conduction
Transmitter synthesis Hemicholiniums Cholinergic nerve terminals: membrane Block uptake of choline and slow
ACh synthesis
α-Methyltyrosine (metyrosine) Adrenergic nerve terminals and adrenal Inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase and
medulla: cytoplasm blocks synthesis of catecholamines
Transmitter storage Vesamicol Cholinergic terminals: VAT on vesicles Prevents storage, depletes
Reserpine, tetrabenazine Adrenergic terminals: VMAT on vesicles Prevents storage, depletes
Transmitter release Many 3 Nerve terminal membrane receptors Modulate release
ω-Conotoxin GVIA 4 Nerve terminal calcium channels Reduces transmitter release
Domoic acid Nerve terminal kainate receptors Modulates transmitter release by
(primarily CNS; see Chapter 21) altering calcium influx/release
Botulinum toxin Cholinergic vesicles Prevents ACh release
α-Latrotoxin 5 Cholinergic and adrenergic vesicles Causes explosive transmitter
release
Tyramine, amphetamine Adrenergic nerve terminals Promote transmitter release
Transmitter reuptake Cocaine, tricyclic Adrenergic nerve terminals, NET Inhibit uptake; increase transmitter
after release antidepressants, SNRI effect on postsynaptic receptors
antidepressants 6
Receptor activation Norepinephrine Receptors at adrenergic junctions Binds and activates α receptors;
or blockade causes contraction
Phentolamine Receptors at adrenergic junctions Binds α receptors; prevents
activation
Isoproterenol Receptors at adrenergic junctions Binds β receptors; activates
adenylyl cyclase
Propranolol Receptors at adrenergic junctions Binds β receptors; prevents
activation
Nicotine Receptors at nicotinic cholinergic Binds nicotinic receptors; opens ion
junctions (autonomic ganglia, channel in postsynaptic membrane
neuromuscular end plates)
Tubocurarine Neuromuscular end plates Prevents activation of nicotinic
receptors
Bethanechol Receptors, parasympathetic Binds and activates muscarinic
effector cells (smooth muscle, glands) receptors
Atropine Receptors, parasympathetic Binds muscarinic receptors;
effector cells prevents activation
Enzymatic inactivation Neostigmine Cholinergic synapses Inhibits enzyme; prolongs and
of transmitter (acetylcholinesterase) intensifies transmitter action after
release
Tranylcypromine Adrenergic nerve terminals Inhibits enzyme; increases stored
(monoamine oxidase) transmitter pool
1
Toxin of puffer fish, California newt.
2 Toxin of Gonyaulax (red tide organism).
3
Norepinephrine, dopamine, acetylcholine, angiotensin II, various prostaglandins, etc.
4 Toxin of marine snails of the genus Conus.
5
Black widow spider venom.
6 Serotonin, norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors.
NET, norepinephrine transporter; SNRI, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors; VAT, vesicle-associated transporter; VMAT, vesicular monoamine transporter.