Page 136 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 136
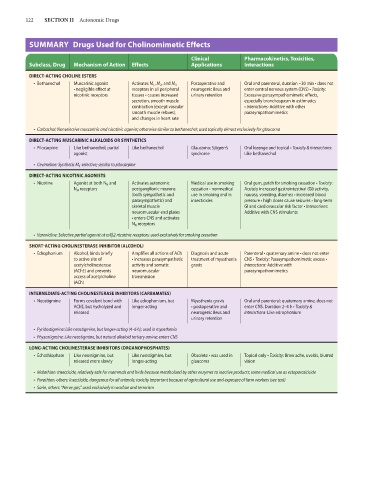
122 SECTION II Autonomic Drugs
SUMMARY Drugs Used for Cholinomimetic Effects
Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Toxicities,
Subclass, Drug Mechanism of Action Effects Applications Interactions
DIRECT-ACTING CHOLINE ESTERS
• Bethanechol Muscarinic agonist Activates M 1 , M 2 , and M 3 Postoperative and Oral and parenteral, duration ~30 min • does not
• negligible effect at receptors in all peripheral neurogenic ileus and enter central nervous system (CNS) • Toxicity:
nicotinic receptors tissues • causes increased urinary retention Excessive parasympathomimetic effects,
secretion, smooth muscle especially bronchospasm in asthmatics
contraction (except vascular • Interactions: Additive with other
smooth muscle relaxes), parasympathomimetics
and changes in heart rate
• Carbachol: Nonselective muscarinic and nicotinic agonist; otherwise similar to bethanechol; used topically almost exclusively for glaucoma
DIRECT-ACTING MUSCARINIC ALKALOIDS OR SYNTHETICS
• Pilocarpine Like bethanechol, partial Like bethanechol Glaucoma; Sjögren’s Oral lozenge and topical • Toxicity & interactions:
agonist syndrome Like bethanechol
• Cevimeline: Synthetic M 3 -selective; similar to pilocarpine
DIRECT-ACTING NICOTINIC AGONISTS
• Nicotine Agonist at both N N and Activates autonomic Medical use in smoking Oral gum, patch for smoking cessation • Toxicity:
N M receptors postganglionic neurons cessation • nonmedical Acutely increased gastrointestinal (GI) activity,
(both sympathetic and use in smoking and in nausea, vomiting, diarrhea • increased blood
parasympathetic) and insecticides pressure • high doses cause seizures • long-term
skeletal muscle GI and cardiovascular risk factor • Interactions:
neuromuscular end plates Additive with CNS stimulants
• enters CNS and activates
N N receptors
• Varenicline: Selective partial agonist at α4β2 nicotinic receptors; used exclusively for smoking cessation
SHORT-ACTING CHOLINESTERASE INHIBITOR (ALCOHOL)
• Edrophonium Alcohol, binds briefly Amplifies all actions of ACh Diagnosis and acute Parenteral • quaternary amine • does not enter
to active site of • increases parasympathetic treatment of myasthenia CNS • Toxicity: Parasympathomimetic excess •
acetylcholinesterase activity and somatic gravis Interactions: Additive with
(AChE) and prevents neuromuscular parasympathomimetics
access of acetylcholine transmission
(ACh)
INTERMEDIATE-ACTING CHOLINESTERASE INHIBITORS (CARBAMATES)
• Neostigmine Forms covalent bond with Like edrophonium, but Myasthenia gravis Oral and parenteral; quaternary amine, does not
AChE, but hydrolyzed and longer-acting • postoperative and enter CNS. Duration 2–4 h • Toxicity &
released neurogenic ileus and interactions: Like edrophonium
urinary retention
• Pyridostigmine: Like neostigmine, but longer-acting (4–6 h); used in myasthenia
• Physostigmine: Like neostigmine, but natural alkaloid tertiary amine; enters CNS
LONG-ACTING CHOLINESTERASE INHIBITORS (ORGANOPHOSPHATES)
• Echothiophate Like neostigmine, but Like neostigmine, but Obsolete • was used in Topical only • Toxicity: Brow ache, uveitis, blurred
released more slowly longer-acting glaucoma vision
• Malathion: Insecticide, relatively safe for mammals and birds because metabolized by other enzymes to inactive products; some medical use as ectoparasiticide
• Parathion, others: Insecticide, dangerous for all animals; toxicity important because of agricultural use and exposure of farm workers (see text)
• Sarin, others: “Nerve gas,” used exclusively in warfare and terrorism