Page 57 - Ilmu Tanah
P. 57
44 The Chemistry and Fertility of Soils under Tropical Weeds
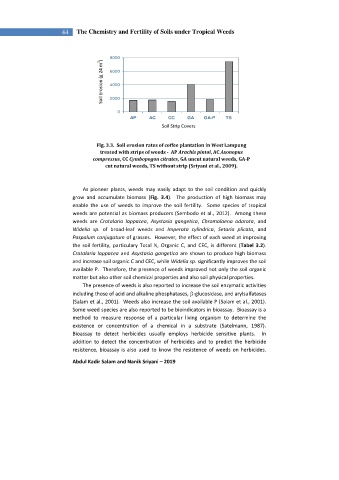
8000
Soil Erosion (g 24 m 2 ) Erosi Tanah (g/24m2) 6000
4000
2000
0
AP AC CC GA GA-P TS
Jenis Strip Penutup Tanah
Soil Strip Covers
Fig. 3.3. Soil erosion rates of coffee plantation in West Lampung
treated with strips of weeds - AP Arachis pintoi, AC Axonopus
compressus, CC Cymbopogon citrates, GA uncut natural weeds, GA-P
cut natural weeds, TS without strip (Sriyani et al., 2009).
As pioneer plants, weeds may easily adapt to the soil condition and quickly
grow and accumulate biomass (Fig. 3.4). The production of high biomass may
enable the use of weeds to improve the soil fertility. Some species of tropical
weeds are potential as biomass producers (Sembodo et al., 2012). Among these
weeds are Crotalaria lappacea, Asystasia gangetica, Chromolaena odorata, and
Widelia sp. of broad-leaf weeds and Imperata cylindrica, Setaria plicata, and
Paspalum conjugatum of grasses. However, the effect of each weed at improving
the soil fertility, particulary Total N, Organic C, and CEC, is different (Tabel 3.2).
Crotalaria lappacea and Asystasia gangetica are shown to produce high biomass
and increase soil organic C and CEC, while Widelia sp. significantly improves the soil
available P. Therefore, the presence of weeds improved not only the soil organic
matter but also other soil chemical properties and also soil physical properties.
The presence of weeds is also reported to increase the soil enzymatic activities
including those of acid and alkaline phosphatases, -glucosidase, and arylsulfatases
(Salam et al., 2001). Weeds also increase the soil available P (Salam et al., 2001).
Some weed species are also reported to be bioindicators in bioassay. Bioassay is a
method to measure response of a particular living organism to determine the
existence or concentration of a chemical in a substrate (Satelmann, 1987).
Bioassay to detect herbicides usually employs herbicide sensitive plants. In
addition to detect the concentration of herbicides and to predict the herbicide
resistence, bioassay is also used to know the resistence of weeds on herbicides.
Abdul Kadir Salam and Nanik Sriyani – 2019