Page 209 - Microeconomics, Fourth Edition
P. 209
c05Thetheoryofdemand.qxd 7/23/10 1:36 PM Page 183
5.4 MARKET DEMAND 183
D = Demand of casual consumer
c
$5 D = Demand of health-conscious consumer
h
D = Market demand
m
P, (dollars per liter) 3 A
4
2
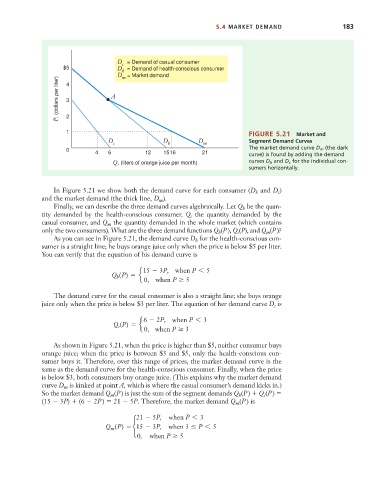
1 FIGURE 5.21 Market and
D c D h D m Segment Demand Curves
0 The market demand curve D m (the dark
4 6 12 1516 21 curve) is found by adding the demand
Q, (liters of orange juice per month) curves D h and D c for the individual con-
sumers horizontally.
In Figure 5.21 we show both the demand curve for each consumer (D and D c )
h
and the market demand (the thick line, D m ).
Finally, we can describe the three demand curves algebraically. Let Q h be the quan-
tity demanded by the health-conscious consumer, Q c the quantity demanded by the
casual consumer, and Q m the quantity demanded in the whole market (which contains
only the two consumers). What are the three demand functions Q h (P), Q c (P), and Q m (P)?
As you can see in Figure 5.21, the demand curve D h for the health-conscious con-
sumer is a straight line; he buys orange juice only when the price is below $5 per liter.
You can verify that the equation of his demand curve is
15 3P, when P 6 5
Q (P) e
b
0, when P 5
The demand curve for the casual consumer is also a straight line; she buys orange
juice only when the price is below $3 per liter. The equation of her demand curve D c is
6 2P, when P 6 3
Q (P) e
c
0, when P 3
As shown in Figure 5.21, when the price is higher than $5, neither consumer buys
orange juice; when the price is between $3 and $5, only the health-conscious con-
sumer buys it. Therefore, over this range of prices, the market demand curve is the
same as the demand curve for the health-conscious consumer. Finally, when the price
is below $3, both consumers buy orange juice. (This explains why the market demand
curve D m is kinked at point A, which is where the casual consumer’s demand kicks in.)
So the market demand Q m (P) is just the sum of the segment demands Q h (P) Q c (P)
(15 3P) (6 2P ) 21 5P. Therefore, the market demand Q m (P ) is
21 5P, when P 6 3
(P) 15 3P, when 3 P 6 5
e
Q m
0, when P 5