Page 751 - Microeconomics, Fourth Edition
P. 751
c17ExternalitiesandPublicGoods.qxd 8/22/10 4:56 AM Page 725
PROBLEMS 725
they have different maximum willingnesses to pay.
MSC
Assume that the graph is drawn to scale.
a) What type of externality is present in this market: pos-
itive or negative?
S b) What is the maximum level of social surplus that is po-
Price of gasoline per week P 1 E B R H G K M MEC c) What is the deadweight loss that arises in a competi-
A
tentially attainable in this market?
tive equilibrium in this market?
P 2
N
d) Suppose a subsidy is given to producers: What
is the magnitude of the subsidy per unit that would
enable this market to attain the socially efficient out-
F
come?
For the remaining questions, please indicate whether
D
the following government interventions would increase
social efficiency relative to the competitive equilibrium
outcome with no government intervention, decrease
Z V
social efficiency, or keep it unchanged:
Q 1 Q 2
e) A subsidy per unit equal to 0F given to consumers who
Gallons of gasoline per week
purchase the good.
(Graph for Problem 17.6)
f ) The government replaces private sellers and offers
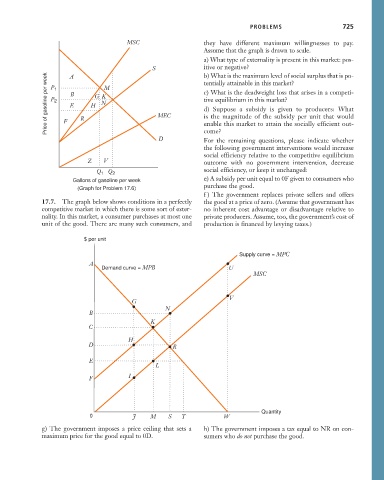
17.7. The graph below shows conditions in a perfectly the good at a price of zero. (Assume that government has
competitive market in which there is some sort of exter- no inherent cost advantage or disadvantage relative to
nality. In this market, a consumer purchases at most one private producers. Assume, too, the government’s cost of
unit of the good. There are many such consumers, and production is financed by levying taxes.)
$ per unit
Supply curve = MPC
A
Demand curve = MPB U
MSC
V
G
N
B
K
C
H
D
R
E
L
I
F
Quantity
0
J M S T W
g) The government imposes a price ceiling that sets a h) The government imposes a tax equal to NR on con-
maximum price for the good equal to 0D. sumers who do not purchase the good.