Page 504 - From GMS to LTE
P. 504
490 From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G
Audio Gateway
Headset (e.g. a mobile phone)
Establishment of the signaling connection
(ACL, L2CAP, RFCOMM, …)
Establishment of the speech channel
(SCO or eSCO)
User presses
‘accept’ button RING
AT + CKPD = 200
OK
Speech connection is established
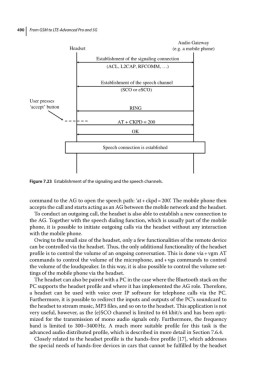
Figure 7.23 Establishment of the signaling and the speech channels.
command to the AG to open the speech path: ‘at + ckpd = 200’. The mobile phone then
accepts the call and starts acting as an AG between the mobile network and the headset.
To conduct an outgoing call, the headset is also able to establish a new connection to
the AG. Together with the speech dialing function, which is usually part of the mobile
phone, it is possible to initiate outgoing calls via the headset without any interaction
with the mobile phone.
Owing to the small size of the headset, only a few functionalities of the remote device
can be controlled via the headset. Thus, the only additional functionality of the headset
profile is to control the volume of an ongoing conversation. This is done via + vgm AT
commands to control the volume of the microphone, and + vgs commands to control
the volume of the loudspeaker. In this way, it is also possible to control the volume set-
tings of the mobile phone via the headset.
The headset can also be paired with a PC in the case where the Bluetooth stack on the
PC supports the headset profile and where it has implemented the AG role. Therefore,
a headset can be used with voice over IP software for telephone calls via the PC.
Furthermore, it is possible to redirect the inputs and outputs of the PC’s soundcard to
the headset to stream music, MP3 files, and so on to the headset. This application is not
very useful, however, as the (e)SCO channel is limited to 64 kbit/s and has been opti-
mized for the transmission of mono audio signals only. Furthermore, the frequency
band is limited to 300–3400 Hz. A much more suitable profile for this task is the
advanced audio distributed profile, which is described in more detail in Section 7.6.4.
Closely related to the headset profile is the hands‐free profile [17], which addresses
the special needs of hands‐free devices in cars that cannot be fulfilled by the headset