Page 444 - Handbook of Modern Telecommunications
P. 444
Network Management and Administration 3-235
Internet Partner
Gateway Gateway
SS7 SS7
Core Core
Switch Switch
Switches Switches
Core Core
Switch Switch
Edge Routers Edge Routers
Data Center 1 Data Center 2
= Probe data collection point
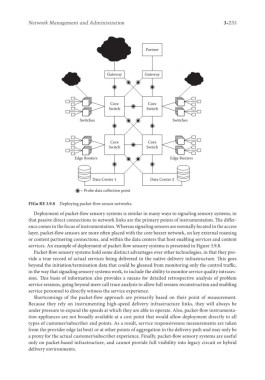
FIGu RE 3.9.8 Deploying packet-flow sensor networks.
Deployment of packet-flow sensory systems is similar in many ways to signaling sensory systems, in
that passive direct connections to network links are the primary points of instrumentation. The differ-
ence comes in the focus of instrumentation. Whereas signaling sensors are normally located in the access
layer, packet-flow sensors are more often placed with the core bearer network, on key external roaming
or content partnering connections, and within the data centers that host enabling services and content
services. An example of deployment of packet-flow sensory systems is presented in Figure 3.9.8.
Packet-flow sensory systems hold some distinct advantages over other technologies, in that they pro-
vide a true record of actual services being delivered in the native delivery infrastructure. This goes
beyond the initiation/termination data that could be gleaned from monitoring only the control traffic,
in the way that signaling sensory systems work, to include the ability to monitor service quality intrases-
sion. This basis of information also provides a means for detailed retrospective analysis of problem
service sessions, going beyond mere call trace analysis to allow full session reconstruction and enabling
service personnel to directly witness the service experience.
Shortcomings of the packet-flow approach are primarily based on their point of measurement.
Because they rely on instrumenting high-speed delivery infrastructure links, they will always be
under pressure to expand the speeds at which they are able to operate. Also, packet-flow instrumenta-
tion appliances are not broadly available at a cost point that would allow deployment directly to all
types of customer/subscriber end points. As a result, service responsiveness measurements are taken
from the provider edge (at best) or at other points of aggregation in the delivery path and may only be
a proxy for the actual customer/subscriber experience. Finally, packet-flow sensory systems are useful
only on packet-based infrastructure, and cannot provide full visibility into legacy circuit or hybrid
delivery environments.