Page 136 - Environment: The Science Behind the Stories
P. 136
Store water
and regulate
water flow Regulate
climate
Purify Provide timber
water and other Purify
Form resources air Cycle
soil
nutrients
Provide Provide
habitat recreation
Control Provide
erosion food
Pollinate
plants
Provide
pest Dampen
control impacts from
disturbance
Filter runoff
and treat
waste
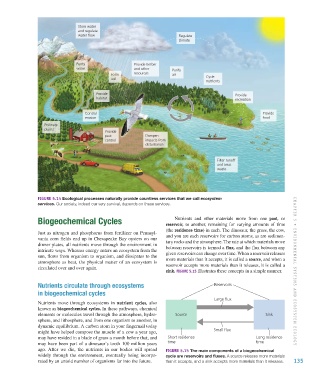
Figure 5.14 Ecological processes naturally provide countless services that we call ecosystem
services. Our society, indeed our very survival, depends on these services.
Nutrients and other materials move from one pool, or
Biogeochemical Cycles reservoir, to another, remaining for varying amounts of time
(the residence time) in each. The dinosaur, the grass, the cow,
Just as nitrogen and phosphorus from fertilizer on Pennsyl- and you are each reservoirs for carbon atoms, as are sedimen-
vania corn fields end up in Chesapeake Bay oysters on our tary rocks and the atmosphere. The rate at which materials move
dinner plates, all nutrients move through the environment in between reservoirs is termed a flux, and the flux between any
intricate ways. Whereas energy enters an ecosystem from the given reservoirs can change over time. When a reservoir releases
sun, flows from organism to organism, and dissipates to the more materials than it accepts, it is called a source, and when a
atmosphere as heat, the physical matter of an ecosystem is reservoir accepts more materials than it releases, it is called a
circulated over and over again.
sink. Figure 5.15 illustrates these concepts in a simple manner. CHAPTER 5 • Envi R onm E n TA l S y STE m S A nd E C o S y STE m E C ology
Nutrients circulate through ecosystems Reservoirs
in biogeochemical cycles
Large flux
Nutrients move through ecosystems in nutrient cycles, also
known as biogeochemical cycles. In these pathways, chemical
elements or molecules travel through the atmosphere, hydro- Source Sink
sphere, and lithosphere, and from one organism to another, in
dynamic equilibrium. A carbon atom in your fingernail today
might have helped compose the muscle of a cow a year ago, Small flux
may have resided in a blade of grass a month before that, and Short residence Long residence
may have been part of a dinosaur’s tooth 100 million years time time
ago. After we die, the nutrients in our bodies will spread Figure 5.15 The main components of a biogeochemical
widely through the environment, eventually being incorpo- cycle are reservoirs and fluxes. A source releases more materials
rated by an untold number of organisms far into the future. than it accepts, and a sink accepts more materials than it releases. 135
M05_WITH7428_05_SE_C05.indd 135 12/12/14 2:56 PM