Page 142 - Environment: The Science Behind the Stories
P. 142
)
Atmosphere (N 2
Fixation
Fixation Dust from
150
150 land
Volatilization
Volatilization
PrecipitationPrecipitation Denitrification
Denitrification
300
67 300
67
NO 2 – Atmosphere (N 2 )
+
NH 3 NH 4 – 3,870,000,000
NO 3
Denitrification
Denitrification
Producers Consumers 81
81
Biotic
Biotic
cycling
cycling Emissions
Emissions
Fixation
8000
8000 Fixation
(NO ) 20) 20
by lightning
Decomposers (NO X X by lightning
4 4
Oceans
Rivers
Natural
Consumers Land plants Natural
biological
Runoff 58 biological
Runoff 58
fixation
fixation
Fixation by
Fixation by 120
100
Assimilation
crops (60)
crops (60) Assimilation
1,200
and fertilizer
Industry and and fertilizer Decomposition 1,200
Decomposition
production (≥136) and waste
automobiles production (≥136) and waste
_
NO
Oceans Deposition in NH 4 + NO 2 _
Deposition in
Nitrification
precipitation Nitrification 3
precipitation
Bacterial conversion
Bacterial conversion
Inorganic N
720,000 Extraction and GroundwaterGroundwater Soil organic matter (NH 3 )
Extraction and
infiltration
combustion infiltration 115,000
combustion
118
118
Burial 10 Groundwater
Burial 10
Fossil fuels
Sediments and sedimentary rock
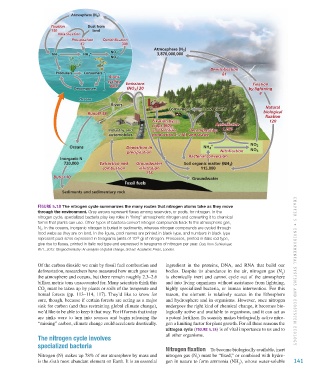
Figure 5.18 The nitrogen cycle summarizes the many routes that nitrogen atoms take as they move
through the environment. Gray arrows represent fluxes among reservoirs, or pools, for nitrogen. In the
nitrogen cycle, specialized bacteria play key roles in “fixing” atmospheric nitrogen and converting it to chemical
forms that plants can use. Other types of bacteria convert nitrogen compounds back to the atmospheric gas,
N . In the oceans, inorganic nitrogen is buried in sediments, whereas nitrogen compounds are cycled through
2
food webs as they are on land. In the figure, pool names are printed in black type, and numbers in black type
represent pool sizes expressed in teragrams (units of 10 g) of nitrogen. Processes, printed in italic red type,
12
give rise to fluxes, printed in italic red type and expressed in teragrams of nitrogen per year. Data from Schlesinger,
W.H., 2013. Biogeochemistry: An analysis of global change, 3rd ed. Academic Press, London.
Of the carbon dioxide we emit by fossil fuel combustion and ingredient in the proteins, DNA, and RNA that build our
deforestation, researchers have measured how much goes into bodies. Despite its abundance in the air, nitrogen gas (N ) CHAPTER 5 • Envi R onm E n TA l S y STE m S A nd E C o S y STE m E C ology
2
the atmosphere and oceans, but there remain roughly 2.3–2.6 is chemically inert and cannot cycle out of the atmosphere
billion metric tons unaccounted for. Many scientists think this and into living organisms without assistance from lightning,
CO must be taken up by plants or soils of the temperate and highly specialized bacteria, or human intervention. For this
2
boreal forests (pp. 113–114, 117). They’d like to know for reason, the element is relatively scarce in the lithosphere
sure, though, because if certain forests are acting as a major and hydrosphere and in organisms. However, once nitrogen
sink for carbon (and thus restraining global climate change), undergoes the right kind of chemical change, it becomes bio-
we’d like to be able to keep it that way. For if forests that today logically active and available to organisms, and it can act as
are sinks were to turn into sources and begin releasing the a potent fertilizer. Its scarcity makes biologically active nitro-
“missing” carbon, climate change could accelerate drastically. gen a limiting factor for plant growth. For all these reasons the
nitrogen cycle (Figure 5.18) is of vital importance to us and to
The nitrogen cycle involves all other organisms.
specialized bacteria
Nitrogen fixation To become biologically available, inert
Nitrogen (N) makes up 78% of our atmosphere by mass and nitrogen gas (N ) must be “fixed,” or combined with hydro-
2
is the sixth most abundant element on Earth. It is an essential gen in nature to form ammonia (NH ), whose water-soluble 141
3
M05_WITH7428_05_SE_C05.indd 141 12/12/14 2:56 PM