Page 226 - Environment: The Science Behind the Stories
P. 226
$50,000 8 Developing countries
$45,000 North America 6 Developed countries
Per-capita income (GNI-PPP 1 ) $30,000 Europe and S. Pacific Global population (billions) 4
$40,000
$35,000
Australia
$25,000
2
$20,000
Latin America
$15,000
$10,000
$5000 and Caribbean 0 1950 1975 2000 2025 2050
Asia Africa Year
$0
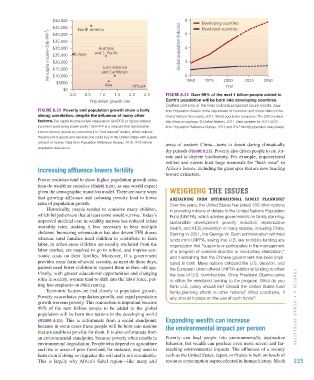
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 Figure 8.21 over 99% of the next 1 billion people added to
Population growth rate Earth’s population will be born into developing countries.
Dashed portions of the lines indicate projected future trends. Data
Figure 8.20 Poverty and population growth show a fairly from Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the
strong correlation, despite the influence of many other United Nations Secretariat, 2011. World population prospects: The 2010 revision.
factors. Per capita income is here measured in GNI PPP, or “gross national http://esa.un.org/wpp. © United Nations, 2011. Data updates for 2011–2012
income in purchasing power parity.” GNI PPP is a measure that standardizes from Population Reference Bureau, 2011 and 2012 World population data sheets.
income among nations by converting it to “international” dollars, which indicate
the amount of goods and services one could buy in the United States with a given
amount of money. Data from Population Reference Bureau, 2010. 2010 World areas of western China—turns to desert during climatically
population data sheet.
dry periods (Figure 8.22). Poverty also drives people to cut for-
ests and to deplete biodiversity. For example, impoverished
settlers and miners hunt large mammals for “bush meat” in
Increasing affluence lowers fertility Africa’s forests, including the great apes that are now heading
toward extinction.
Poorer societies tend to show higher population growth rates
than do wealthier societies (Figure 8.20), as one would expect
given the demographic transition model. There are many ways WEIGHING THE ISSUES
that growing affluence and reducing poverty lead to lower aBSTaINING FROM INTERNaTIONaL FaMILy PLaNNING?
rates of population growth. Over the years, the United States has joined 180 other nations
Historically, people tended to conceive many children, in providing millions of dollars to the United Nations Population
which helped ensure that at least some would survive. Today’s Fund (UNFPA), which advises governments on family planning,
improved medical care in wealthy nations has reduced infant sustainable development, poverty reduction, reproductive
mortality rates, making it less necessary to bear multiple health, and AIDS prevention in many nations, including China.
children. Increasing urbanization has also driven TFR down; Starting in 2001, the George W. Bush administration withheld
whereas rural families need children to contribute to farm funds from UNFPA, saying that U.S. law prohibits funding any
labor, in urban areas children are usually excluded from the organization that “supports or participates in the management
labor market, are required to go to school, and impose eco- of a program of coercive abortion or involuntary sterilization,”
nomic costs on their families. Moreover, if a government and maintaining that the Chinese government has been impli-
provides some form of social security, as most do these days, cated in both. Many nations criticized the U.S. decision, and
parents need fewer children to support them in their old age. the European Union offered UNFPA additional funding to offset
Finally, with greater educational opportunities and changing the loss of U.S. contributions. Once President Obama came
roles in society, women tend to shift into the labor force, put- to office, he reinstated funding to the program. What do you
ting less emphasis on child rearing. think U.S. policy should be? Should the United States fund
Economic factors are tied closely to population growth. family-planning efforts in other nations? What conditions, if
Poverty exacerbates population growth, and rapid population any, should it place on the use of such funds?
growth worsens poverty. This connection is important because
99% of the next billion people to be added to the global CHAPTER 8 • Hum A n Po P ul AT i on
population will be born into nations in the developing world
(Figure 8.21). This is unfortunate from a social standpoint, Expanding wealth can increase
because in some cases these people will be born into nations the environmental impact per person
that are unable to provide for them. It is also unfortunate from
an environmental standpoint, because poverty often results in Poverty can lead people into environmentally destructive
environmental degradation. People who depend on agriculture behavior, but wealth can produce even more severe and far-
and live in areas of poor farmland, for instance, may need to reaching environmental impacts. The affluence of a society
farm even if doing so degrades the soil and is not sustainable. such as the United States, Japan, or France is built on levels of
This is largely why Africa’s Sahel region—like many arid resource consumption unprecedented in human history. Much 225
M08_WITH7428_05_SE_C08.indd 225 12/12/14 2:58 PM