Page 540 - Environment: The Science Behind the Stories
P. 540
power technologies. Solar radiation also helps drive wind 4
and the water cycle, enabling us to harness wind power and
hydroelectric power. And of course, sunlight drives pho- Oil
tosynthesis (p. 50) and the growth of plants, from which 3
we take wood and other biomass as a fuel source. When Coal
plants and other organisms die and are buried in sediments (billion tons of oil equivalent) 2
under particular conditions, their stored chemical energy World fossil fuel consumption
may eventually be transferred to fossil fuels, highly com- Natural gas
bustible substances formed from the remains of organisms 1
from past geologic ages. Today we rely on three main fos-
sil fuels, in the form of a solid (coal), liquid (oil), and gas
(natural gas). 0
In addition, a great deal of energy emanates from Earth’s 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
core, making geothermal power available for our use. Energy Year
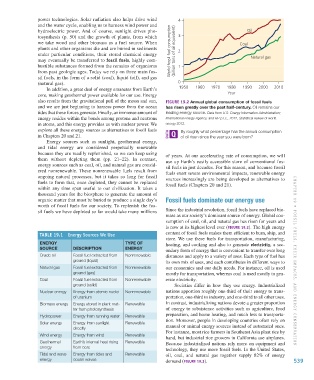
also results from the gravitational pull of the moon and sun, FIGURE 19.2 Annual global consumption of fossil fuels
and we are just beginning to harness power from the ocean has risen greatly over the past half-century. Oil remains our
tides that these forces generate. Finally, an immense amount of leading energy source. Data from U.S. Energy Information Administration;
energy resides within the bonds among protons and neutrons International Energy Agency; and BP p.l.c., 2012, Statistical review of world
in atoms, and this energy provides us with nuclear power. We energy 2012.
explore all these energy sources as alternatives to fossil fuels By roughly what percentage has the annual consumption
in Chapters 20 and 21. of oil risen since the year you were born?
Energy sources such as sunlight, geothermal energy,
and tidal energy are considered perpetually renewable
because they are readily replenished, so we can keep using of years. At our accelerating rate of consumption, we will
them without depleting them (pp. 21–22). In contrast, use up Earth’s easily accessible store of conventional fos-
energy sources such as coal, oil, and natural gas are consid- sil fuels in just decades. For this reason, and because fossil
ered nonrenewable. These nonrenewable fuels result from fuels exert severe environmental impacts, renewable energy
ongoing natural processes, but it takes so long for fossil sources increasingly are being developed as alternatives to
fuels to form that, once depleted, they cannot be replaced fossil fuels (Chapters 20 and 21).
within any time span useful to our civilization. It takes a
thousand years for the biosphere to generate the amount of
organic matter that must be buried to produce a single day’s Fossil fuels dominate our energy use
worth of fossil fuels for our society. To replenish the fos-
sil fuels we have depleted so far would take many millions Since the industrial revolution, fossil fuels have replaced bio-
mass as our society’s dominant source of energy. Global con-
sumption of coal, oil, and natural gas has risen for years and
is now at its highest level ever (FIGURE 19.2). The high energy
TABLE 19.1 Energy Sources We Use content of fossil fuels makes them efficient to burn, ship, and
store. We use these fuels for transportation, manufacturing,
ENERGY TYPE OF heating, and cooking and also to generate electricity, a sec-
SOURCE DESCRIPTION ENERGY
ondary form of energy that is convenient to transfer over long
Crude oil Fossil fuel extracted from Nonrenewable distances and apply to a variety of uses. Each type of fuel has
ground (liquid) its own mix of uses, and each contributes in different ways to CHAPTER 19 • FOSSIL FUELS, THEIR IMPA CT S, AND ENERGY CONSERVATI ON
Natural gas Fossil fuel extracted from Nonrenewable our economies and our daily needs. For instance, oil is used
ground (gas) mostly for transportation, whereas coal is used mostly to gen-
Coal Fossil fuel extracted from Nonrenewable erate electricity.
ground (solid) Societies differ in how they use energy. Industrialized
Nuclear energy Energy from atomic nuclei Nonrenewable nations apportion roughly one-third of their energy to trans-
of uranium portation, one-third to industry, and one-third to all other uses.
Biomass energy Energy stored in plant mat- Renewable In contrast, industrializing nations devote a greater proportion
ter from photosynthesis of energy to subsistence activities such as agriculture, food
Hydropower Energy from running water Renewable preparation, and home heating, and much less to transporta-
tion. Moreover, people in developing countries often rely on
Solar energy Energy from sunlight Renewable
directly manual or animal energy sources instead of automated ones.
For instance, most rice farmers in Southeast Asia plant rice by
Wind energy Energy from wind Renewable
hand, but industrial rice growers in California use airplanes.
Geothermal Earth’s internal heat rising Renewable Because industrialized nations rely more on equipment and
energy from core
technology, they use more fossil fuels. In the United States,
Tidal and wave Energy from tides and Renewable oil, coal, and natural gas together supply 82% of energy
energy ocean waves demand (FIGURE 19.3). 539
M19_WITH7428_05_SE_C19.indd 539 12/12/14 5:22 PM