Page 583 - Basic College Mathematics with Early Integers
P. 583
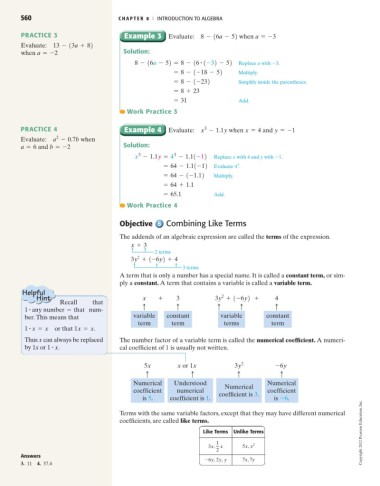
560 C HAPTE R 8 I INTRODUCTION TO ALGEBRA
PRACTICE 3 Example 3 Evaluate: 8 - 16a - 52 when a =-3
Evaluate: 13 - 13a + 82
when a =-2 Solution:
#
8 - 16a - 52 = 8 - 16 1-32 - 52 Replace a with -3.
= 8 - 1-18 - 52 Multiply.
= 8 - 1-232 Simplify inside the parentheses.
= 8 + 23
= 31 Add.
Work Practice 3
3
PRACTICE 4 Example 4 Evaluate: x - 1.1y when x = 4 and y =-1
2
Evaluate: a - 0.7b when
a = 6 and b =-2 Solution:
3 3
x - 1.1y = 4 - 1.11-12 Replace x with 4 and y with -1.
3
= 64 - 1.11-12 Evaluate 4 .
= 64 - 1-1.12 Multiply.
= 64 + 1.1
= 65.1 Add.
Work Practice 4
Objective Combining Like Terms
The addends of an algebraic expression are called the terms of the expression.
x+3
2 terms
2
3y +(–6y)+4
3 terms
A term that is only a number has a special name. It is called a constant term, or sim-
ply a constant. A term that contains a variable is called a variable term.
2
x + 3 3y + 1-6y2 + 4
Recall that
#
1 any number = that num- c c c c c
ber.This means that variable constant variable constant
term term terms term
#
1 x = x or that 1x = x.
Thus x can always be replaced The number factor of a variable term is called the numerical coefficient. A numeri-
#
by 1x or 1 x. cal coefficient of 1 is usually not written.
5x x or 1x 3y 2 -6y
c c c c
Numerical Understood Numerical
Numerical
coefficient numerical coefficient
coefficient is 3.
is 5. coefficient is 1. is -6.
Terms with the same variable factors, except that they may have different numerical
coefficients, are called like terms.
Like Terms Unlike Terms Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
1
3x, x 5x, x 2
2
Answers
-6y, 2y, y 7x,7y
3. 11 4. 37.4