Page 199 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 199
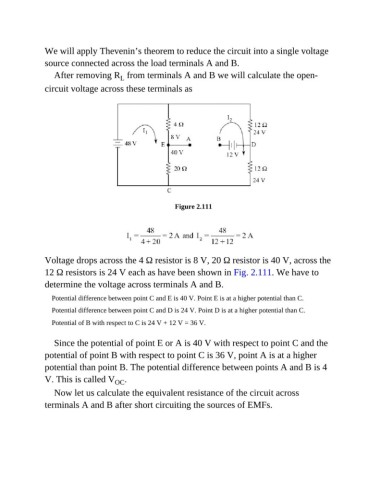
We will apply Thevenin’s theorem to reduce the circuit into a single voltage
source connected across the load terminals A and B.
After removing R from terminals A and B we will calculate the open-
L
circuit voltage across these terminals as
Figure 2.111
Voltage drops across the 4 Ω resistor is 8 V, 20 Ω resistor is 40 V, across the
12 Ω resistors is 24 V each as have been shown in Fig. 2.111. We have to
determine the voltage across terminals A and B.
Potential difference between point C and E is 40 V. Point E is at a higher potential than C.
Potential difference between point C and D is 24 V. Point D is at a higher potential than C.
Potential of B with respect to C is 24 V + 12 V = 36 V.
Since the potential of point E or A is 40 V with respect to point C and the
potential of point B with respect to point C is 36 V, point A is at a higher
potential than point B. The potential difference between points A and B is 4
V. This is called V OC .
Now let us calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit across
terminals A and B after short circuiting the sources of EMFs.