Page 287 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 287
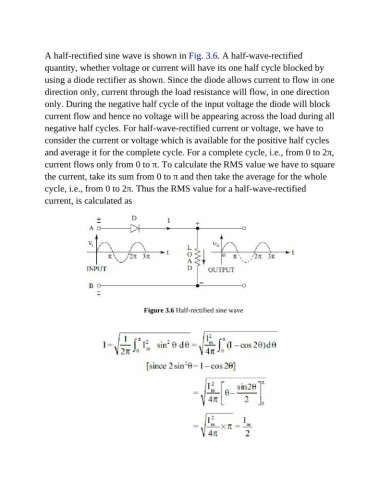
A half-rectified sine wave is shown in Fig. 3.6. A half-wave-rectified
quantity, whether voltage or current will have its one half cycle blocked by
using a diode rectifier as shown. Since the diode allows current to flow in one
direction only, current through the load resistance will flow, in one direction
only. During the negative half cycle of the input voltage the diode will block
current flow and hence no voltage will be appearing across the load during all
negative half cycles. For half-wave-rectified current or voltage, we have to
consider the current or voltage which is available for the positive half cycles
and average it for the complete cycle. For a complete cycle, i.e., from 0 to 2π,
current flows only from 0 to π. To calculate the RMS value we have to square
the current, take its sum from 0 to π and then take the average for the whole
cycle, i.e., from 0 to 2π. Thus the RMS value for a half-wave-rectified
current, is calculated as
Figure 3.6 Half-rectified sine wave