Page 497 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 497
5.6 COMPARISON BETWEEN MAGNETIC AND ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
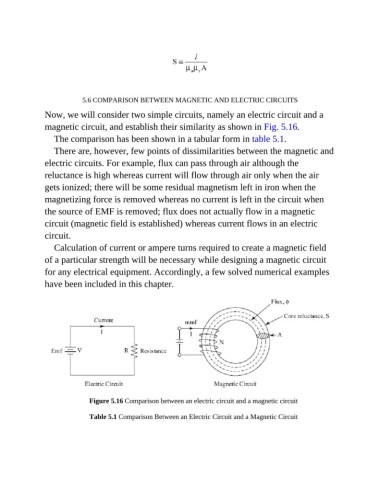
Now, we will consider two simple circuits, namely an electric circuit and a
magnetic circuit, and establish their similarity as shown in Fig. 5.16.
The comparison has been shown in a tabular form in table 5.1.
There are, however, few points of dissimilarities between the magnetic and
electric circuits. For example, flux can pass through air although the
reluctance is high whereas current will flow through air only when the air
gets ionized; there will be some residual magnetism left in iron when the
magnetizing force is removed whereas no current is left in the circuit when
the source of EMF is removed; flux does not actually flow in a magnetic
circuit (magnetic field is established) whereas current flows in an electric
circuit.
Calculation of current or ampere turns required to create a magnetic field
of a particular strength will be necessary while designing a magnetic circuit
for any electrical equipment. Accordingly, a few solved numerical examples
have been included in this chapter.
Figure 5.16 Comparison between an electric circuit and a magnetic circuit
Table 5.1 Comparison Between an Electric Circuit and a Magnetic Circuit