Page 286 - Using MIS
P. 286
254 Chapter 7 Processes, Organizations, and Information Systems
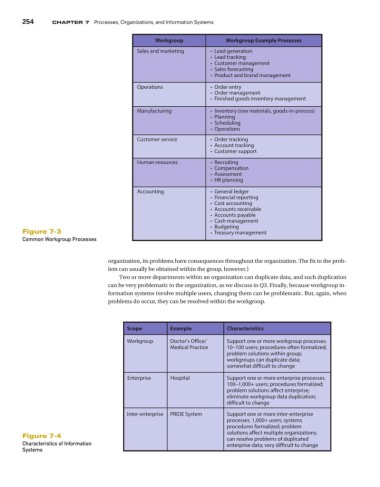
Workgroup Workgroup Example Processes
Sales and marketing • Lead generation
• Lead tracking
• Customer management
• Sales forecasting
• Product and brand management
Operations • Order entry
• Order management
• Finished goods inventory management
Manufacturing • Inventory (raw materials, goods-in-process)
• Planning
• Scheduling
• Operations
Customer service • Order tracking
• Account tracking
• Customer support
Human resources • Recruiting
• Compensation
• Assessment
• HR planning
Accounting • General ledger
• Financial reporting
• Cost accounting
• Accounts receivable
• Accounts payable
• Cash management
• Budgeting
Figure 7-3 • Treasury management
Common Workgroup Processes
organization, its problems have consequences throughout the organization. The fix to the prob-
lem can usually be obtained within the group, however.)
Two or more departments within an organization can duplicate data, and such duplication
can be very problematic to the organization, as we discuss in Q3. Finally, because workgroup in-
formation systems involve multiple users, changing them can be problematic. But, again, when
problems do occur, they can be resolved within the workgroup.
Scope Example Characteristics
Workgroup Doctor's Office/ Support one or more workgroup processes.
Medical Practice 10–100 users; procedures often formalized;
problem solutions within group;
workgroups can duplicate data;
somewhat difficult to change
Enterprise Hospital Support one or more enterprise processes.
100–1,000+ users; procedures formalized;
problem solutions affect enterprise;
eliminate workgroup data duplication;
difficult to change
Inter-enterprise PRIDE System Support one or more inter-enterprise
processes. 1,000+ users; systems
procedures formalized; problem
solutions affect multiple organizations;
Figure 7-4 can resolve problems of duplicated
Characteristics of Information enterprise data; very difficult to change
Systems