Page 424 - Using MIS
P. 424
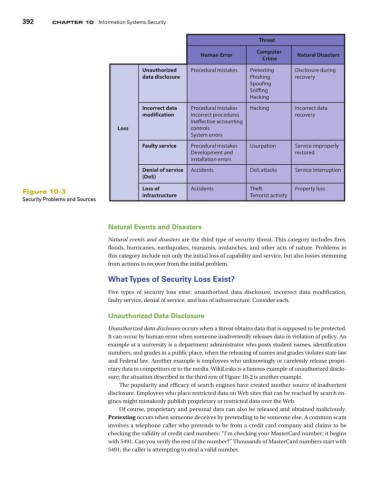
392 Chapter 10 Information Systems Security
Threat
Computer
Human Error Natural Disasters
Crime
Unauthorized Procedural mistakes Pretexting Disclosure during
data disclosure Phishing recovery
Spoofing
Sniffing
Hacking
Incorrect data Procedural mistakes Hacking Incorrect data
modification Incorrect procedures recovery
Ineective accounting
Loss controls
System errors
Faulty service Procedural mistakes Usurpation Service improperly
Development and restored
installation errors
Denial of service Accidents DoS attacks Service interruption
(DoS)
Loss of Accidents Theft Property loss
Figure 10-3 infrastructure Terrorist activity
Security Problems and Sources
Natural Events and Disasters
Natural events and disasters are the third type of security threat. This category includes fires,
floods, hurricanes, earthquakes, tsunamis, avalanches, and other acts of nature. Problems in
this category include not only the initial loss of capability and service, but also losses stemming
from actions to recover from the initial problem.
What Types of Security Loss Exist?
Five types of security loss exist: unauthorized data disclosure, incorrect data modification,
faulty service, denial of service, and loss of infrastructure. Consider each.
Unauthorized Data Disclosure
Unauthorized data disclosure occurs when a threat obtains data that is supposed to be protected.
It can occur by human error when someone inadvertently releases data in violation of policy. An
example at a university is a department administrator who posts student names, identification
numbers, and grades in a public place, when the releasing of names and grades violates state law
and Federal law. Another example is employees who unknowingly or carelessly release propri-
etary data to competitors or to the media. WikiLeaks is a famous example of unauthorized disclo-
sure; the situation described in the third row of Figure 10-2 is another example.
The popularity and efficacy of search engines have created another source of inadvertent
disclosure. Employees who place restricted data on Web sites that can be reached by search en-
gines might mistakenly publish proprietary or restricted data over the Web.
Of course, proprietary and personal data can also be released and obtained maliciously.
Pretexting occurs when someone deceives by pretending to be someone else. A common scam
involves a telephone caller who pretends to be from a credit card company and claims to be
checking the validity of credit card numbers: “I’m checking your MasterCard number; it begins
with 5491. Can you verify the rest of the number?” Thousands of MasterCard numbers start with
5491; the caller is attempting to steal a valid number.