Page 23 - CCFA Journal - Tenth Issue
P. 23
加中金融 风险管理 Risk Management
加中金融
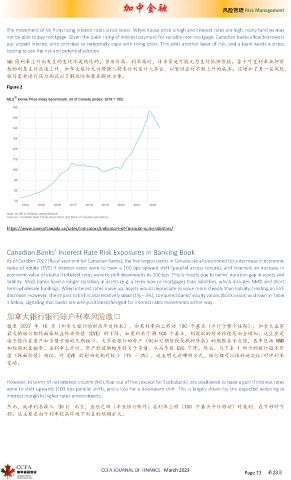
The movement of NII from rising interest rates is not linear. When house price is high and interest rates are high, many families may
not be able to pay mortgage. Given the quick rising of interest payment for variable rate mortgage, Canadian banks allow borrowers
put unpaid interest onto principal to temporally cope with rising costs. This adds another layer of risk, and a bank needs a stress
testing to see the risk and potential solution.
NII 因利率上升而发生的变化不是线性的。当房价高、利率高时,许多家庭可能无力支付抵押贷款。鉴于可变利率抵押贷
款的利息支付迅速上升,加拿大银行允许借款人将未付利息计入本金,以暂时应对不断上升的成本。这增加了另一层风险,
银行需要进行压力测试以了解风险和潜在解决方案。
Figure 2
https://www.bankofcanada.ca/rates/indicators/indicators-of-financial-vulnerabilities/
Canadian Banks’ Interest Rate Risk Exposures in Banking Book
As of October 2022 (fiscal year end for Canadian Banks), the five largest banks in Canada are all positioned for a decrease in economic
value of equity (EVE) if interest rates were to have a 100 bps upward shift (parallel across tenure), and inversely an increase in
economic value of equity if interest rates were to shift downwards by 100 bps. This is mostly due to banks’ duration gap in assets and
liability. Most banks have a longer duration in assets (e.g. a term loan or mortgage) than liabilities, which includes NMD and short
term wholesale fundings. When interest rates move up, assets would depreciate in value more steeply than liability creating an EVE
decrease. However, the impact to EVE is also relatively small (1% – 3%), compared banks’ equity values (book value) as shown in Table
1 below, signaling that banks are well positioned/hedged for interest rates movements either way.
加拿大银行银行账户利率风险敞口
截至 2022 年 10 月(加拿大银行的财政年度结束),如果利率向上移动 100 个基点(平行于整个任期),加拿大五家
最大的银行都将面临权益经济价值 (EVE) 的下降,如果利率下调 100 个基点,则股权的经济价值反而会增加。这主要是
由于银行在资产和负债方面的久期缺口。大多数银行的资产(例如定期贷款或抵押贷款)的期限长于负债,其中包括 NMD
和短期批发融资。当利率上升时,资产贬值的幅度将大于负债,从而导致 EVE 下降。然而,与下表 1 所示的银行股本价
值(账面价值)相比,对 EVE 的影响也相对较小(1% - 3%),这表明无论哪种方式,银行都可以很好地定位/对冲利率
变动。
However, in terms of net interest income (NII), four out of five (except for Scotiabank), are positioned to have a gain if interest rates
were to shift upwards (100 bps parallel shift), and a loss for a downward shift. This is largely driven by the expected widening in
interest margin in higher rates environments.
然而,就净利息收入 (NII) 而言,五分之四(丰业银行除外)在利率上移(100 个基点平行移动)时获利,在下移时亏
损。这主要是由于利率较高环境下利差的预期扩大。
CCFA JOURNAL OF FINANCE March 2023
Page 23 第23页