Page 47 - FINAL CFA II SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 8
P. 47
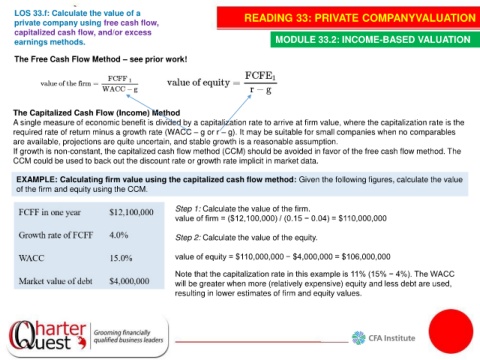
LOS 33.f: Calculate the value of a READING 33: PRIVATE COMPANYVALUATION
private company using free cash flow,
capitalized cash flow, and/or excess
earnings methods. MODULE 33.2: INCOME-BASED VALUATION
The Free Cash Flow Method – see prior work!
The Capitalized Cash Flow (Income) Method
A single measure of economic benefit is divided by a capitalization rate to arrive at firm value, where the capitalization rate is the
required rate of return minus a growth rate (WACC – g or r – g). It may be suitable for small companies when no comparables
are available, projections are quite uncertain, and stable growth is a reasonable assumption.
If growth is non-constant, the capitalized cash flow method (CCM) should be avoided in favor of the free cash flow method. The
CCM could be used to back out the discount rate or growth rate implicit in market data.
EXAMPLE: Calculating firm value using the capitalized cash flow method: Given the following figures, calculate the value
of the firm and equity using the CCM.
Step 1: Calculate the value of the firm.
value of firm = ($12,100,000) / (0.15 − 0.04) = $110,000,000
Step 2: Calculate the value of the equity.
value of equity = $110,000,000 − $4,000,000 = $106,000,000
Note that the capitalization rate in this example is 11% (15% − 4%). The WACC
will be greater when more (relatively expensive) equity and less debt are used,
resulting in lower estimates of firm and equity values.