Page 17 - FINAL CFA SLIDES DECEMBER 2018 DAY 13
P. 17
Session Unit 13:
44. Market Structure & organisation
LOS 44.i: Define primary and secondary markets and explain how secondary markets support primary markets., p.205
Primary Markets: For new issues of securities, which could be:
• Seasoned offerings or secondary issues if company is already listed and its shares trading
• Initial Public Offering (IPO) if it’s the first time the company is going public!
Secondary markets: Where securities trade after their first issuance –their importance is the liquidity and price/value
information they provide!
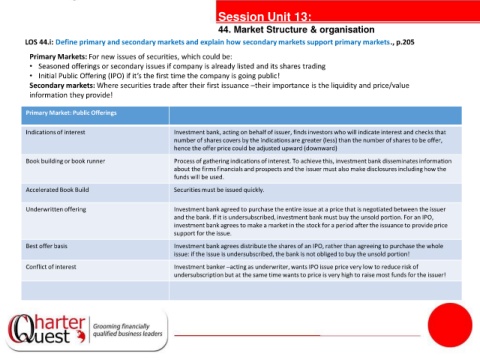
Primary Market: Public Offerings
Indications of interest Investment bank, acting on behalf of issuer, finds investors who will indicate interest and checks that
number of shares covers by the indications are greater (less) than the number of shares to be offer,
hence the offer price could be adjusted upward (downward)
Book building or book runner Process of gathering indications of interest. To achieve this, investment bank disseminates information
tantiesthe issuer must also make disclosures including how the
about the firms financials and prospects and
funds will be used.
Accelerated Book Build Securities must be issued quickly.
Underwritten offering Investment bank agreed to purchase the entire issue at a price that is negotiated between the issuer
and the bank. If it is undersubscribed, investment bank must buy the unsold portion. For an IPO,
investment bank agrees to make a market in the stock for a period after the issuance to provide price
support for the issue.
Best offer basis Investment bank agrees distribute the shares of an IPO, rather than agreeing to purchase the whole
issue: if the issue is undersubscribed, the bank is not obliged to buy the unsold portion!
Conflict of interest Investment banker –acting as underwriter, wants IPO issue price very low to reduce risk of
undersubscription but at the same time wants to price is very high to raise most funds for the issuer!