Page 232 - Microsoft Word - 00 CIMA F1 Prelims STUDENT 2018.docx
P. 232
Subject P2: Advanced Management Accounting
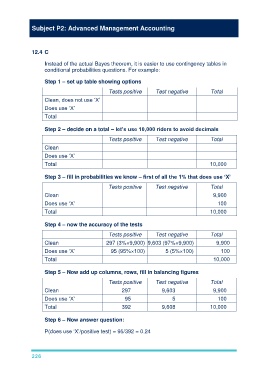
12.4 C
Instead of the actual Bayes theorem, it is easier to use contingency tables in
conditional probabilities questions. For example:
Step 1 – set up table showing options
Tests positive Test negative Total
Clean, does not use ‘X’
Does use ‘X’
Total
Step 2 – decide on a total – let’s use 10,000 riders to avoid decimals
Tests positive Test negative Total
Clean
Does use ‘X’
Total 10,000
Step 3 – fill in probabilities we know – first of all the 1% that does use ‘X’
Tests positive Test negative Total
Clean 9,900
Does use ‘X’ 100
Total 10,000
Step 4 – now the accuracy of the tests
Tests positive Test negative Total
Clean 297 (3%×9,900) 9,603 (97%×9,900) 9,900
Does use ‘X’ 95 (95%×100) 5 (5%×100) 100
Total 10,000
Step 5 – Now add up columns, rows, fill in balancing figures
Tests positive Test negative Total
Clean 297 9,603 9,900
Does use ‘X’ 95 5 100
Total 392 9,608 10,000
Step 6 – Now answer question:
P(does use ‘X’/positive test) = 95/392 = 0.24
226