Page 13 - CSEB Report
P. 13
Study on Compressed Stabilized Earth Blocks
4.1 Compressive Strength and Water Absorption
The compressive strength is the most universally accepted value for determining the quality
of bricks. Nevertheless, it is intensely related with the soil types and the content of
stabilizer. The crushing strength of the blocks were tested using the universal testing
machine. A total of 72 specimens were prepared and crushed at 28days.
In addition, water absorption tests were also conducted to determine durability behaviour
of bricks in weathering. The degree of compactness of bricks can be obtained by water
absorption test, as water is absorbed by pores in bricks. Regarding the water absorption
of Red bricks, [2] states that the bricks shall not have water absorption more that 20% by
weight and for first class bricks, the value shall be less than or in the range of 12% to
15% by weight.
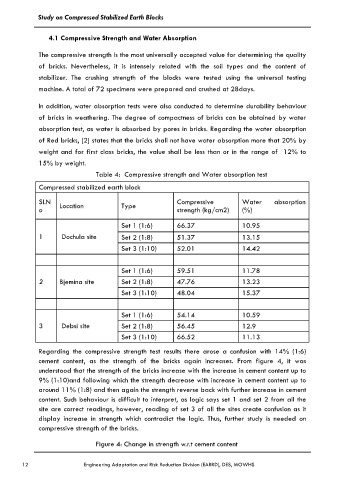
Table 4: Compressive strength and Water absorption test
Compressed stabilized earth block
SI.N Location Type Compressive Water absorption
o strength (kg/cm2) (%)
Set 1 (1:6) 66.37 10.95
1 Dochula site Set 2 (1:8) 51.37 13.15
Set 3 (1:10) 52.01 14.42
Set 1 (1:6) 59.51 11.78
2 Bjemina site Set 2 (1:8) 47.76 13.23
Set 3 (1:10) 48.04 15.37
Set 1 (1:6) 54.14 10.59
3 Debsi site Set 2 (1:8) 56.45 12.9
Set 3 (1:10) 66.52 11.13
Regarding the compressive strength test results there arose a confusion with 14% (1:6)
cement content, as the strength of the bricks again increases. From figure 4, it was
understood that the strength of the bricks increase with the increase in cement content up to
9% (1:10)and following which the strength decrease with increase in cement content up to
around 11% (1:8) and then again the strength reverse back with further increase in cement
content. Such behaviour is difficult to interpret, as logic says set 1 and set 2 from all the
site are correct readings, however, reading of set 3 of all the sites create confusion as it
display increase in strength which contradict the logic. Thus, further study is needed on
compressive strength of the bricks.
Figure 4: Change in strength w.r.t cement content
12 Engineering Adaptation and Risk Reduction Division (EARRD), DES, MOWHS