Page 165 - phytochemistry I - PharmD Clinical
P. 165
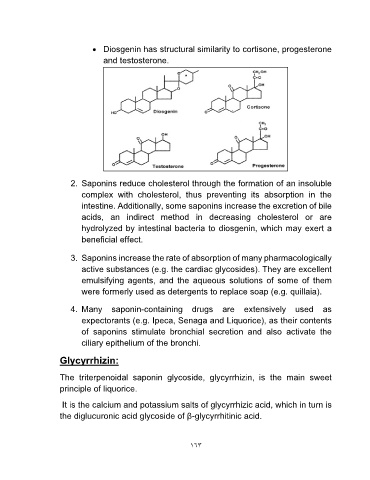
• Diosgenin has structural similarity to cortisone, progesterone
and testosterone.
2. Saponins reduce cholesterol through the formation of an insoluble
complex with cholesterol, thus preventing its absorption in the
intestine. Additionally, some saponins increase the excretion of bile
acids, an indirect method in decreasing cholesterol or are
hydrolyzed by intestinal bacteria to diosgenin, which may exert a
beneficial effect.
3. Saponins increase the rate of absorption of many pharmacologically
active substances (e.g. the cardiac glycosides). They are excellent
emulsifying agents, and the aqueous solutions of some of them
were formerly used as detergents to replace soap (e.g. quillaia).
4. Many saponin-containing drugs are extensively used as
expectorants (e.g. Ipeca, Senaga and Liquorice), as their contents
of saponins stimulate bronchial secretion and also activate the
ciliary epithelium of the bronchi.
Glycyrrhizin:
The triterpenoidal saponin glycoside, glycyrrhizin, is the main sweet
principle of liquorice.
It is the calcium and potassium salts of glycyrrhizic acid, which in turn is
the diglucuronic acid glycoside of β-glycyrrhitinic acid.
۱٦۳