Page 14 - 14th @ Irving Basis of Design (internal)
P. 14
2.2.3 SYSTEM OPPORTUNITIES
HVAC SYSTEM SELECTION
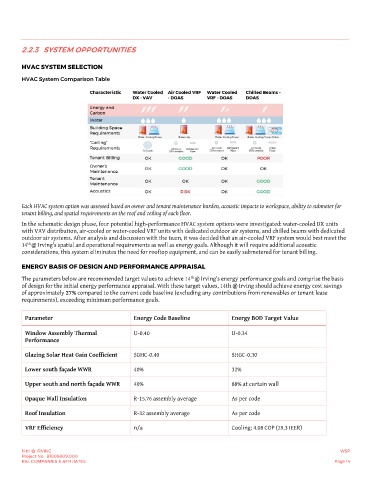
HVAC System Comparison Table
Each HVAC system option was assessed based on owner and tenant maintenance burden, acoustic impacts to workspace, ability to submeter for
tenant billing, and spatial requirements on the roof and ceiling of each floor.
In the schematic design phase, four potential high-performance HVAC system options were investigated: water-cooled DX units
with VAV distribution, air-cooled or water-cooled VRF units with dedicated outdoor air systems, and chilled beams with dedicated
outdoor air systems. After analysis and discussion with the team, it was decided that an air-cooled VRF system would best meet the
th
14 @ Irving’s spatial and operational requirements as well as energy goals. Although it will require additional acoustic
considerations, this system eliminates the need for rooftop equipment, and can be easily submetered for tenant billing.
ENERGY BASIS OF DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL
The parameters below are recommended target values to achieve 14 @ Irving’s energy performance goals and comprise the basis
th
of design for the initial energy performance appraisal. With these target values, 14th @ Irving should achieve energy cost savings
of approximately 27% compared to the current code baseline (excluding any contributions from renewables or tenant lease
requirements), exceeding minimum performance goals.
Parameter Energy Code Baseline Energy BOD Target Value
Window Assembly Thermal U-0.40 U-0.34
Performance
Glazing Solar Heat Gain Coefficient SGHC-0.40 SHGC-0.30
Lower south façade WWR 40% 32%
Upper south and north façade WWR 40% 88% at curtain wall
Opaque Wall Insulation R-15.76 assembly average As per code
Roof Insulation R-32 assembly average As per code
VRF Efficiency n/a Cooling: 4.08 COP (29.3 IEER)
14th @ IRVING WSP
Project No. B1809809.000
RAL COMPANIES & AFFILIATES Page 14