Page 39 - International Marketing
P. 39
NPP
BRILLIANT'S Introduction to International Marketing 41
Factor Endowments
Policy System
Intermediate
products
Immobile Mobile
Market Failure
Structural Transactional
Entry Government Spatial Common Scale Conginitive
Barriers Intervention Governance (Risk lack
(externalities) of information)
14
Oa O t 13
1 L etc. etc. I 12
2 O etc. 11
3 5 etc.
4 6 9 10
8
Structural 7
Variables
Country Industry Firm
Developed-Developing High-Low technology Size
Large-Small Innovatory-Matre Age
Degree of Industralization Processing-Accesibility Strategy
etc. Competitive-Monopolistic Leader-Flower
etc. Innovator-Imitator
etc.
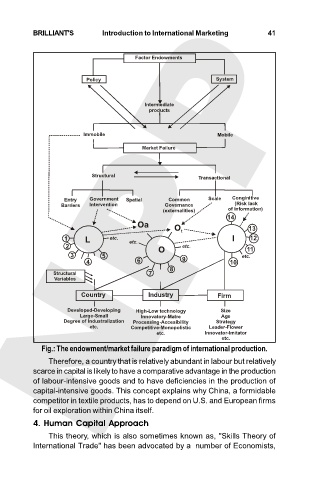
Fig.: The endowment/market failure paradigm of international production.
Therefore, a country that is relatively abundant in labour but relatively
scarce in capital is likely to have a comparative advantage in the production
of labour-intensive goods and to have deficiencies in the production of
capital-intensive goods. This concept explains why China, a formidable
competitor in textile products, has to depend on U.S. and European firms
for oil exploration within China itself.
4. Human Capital Approach
This theory, which is also sometimes known as, "Skills Theory of
International Trade" has been advocated by a number of Economists,