Page 62 - ro membanes
P. 62
3.2 TYPICAL MEMBRANE-FOULING PHENOMENA 45
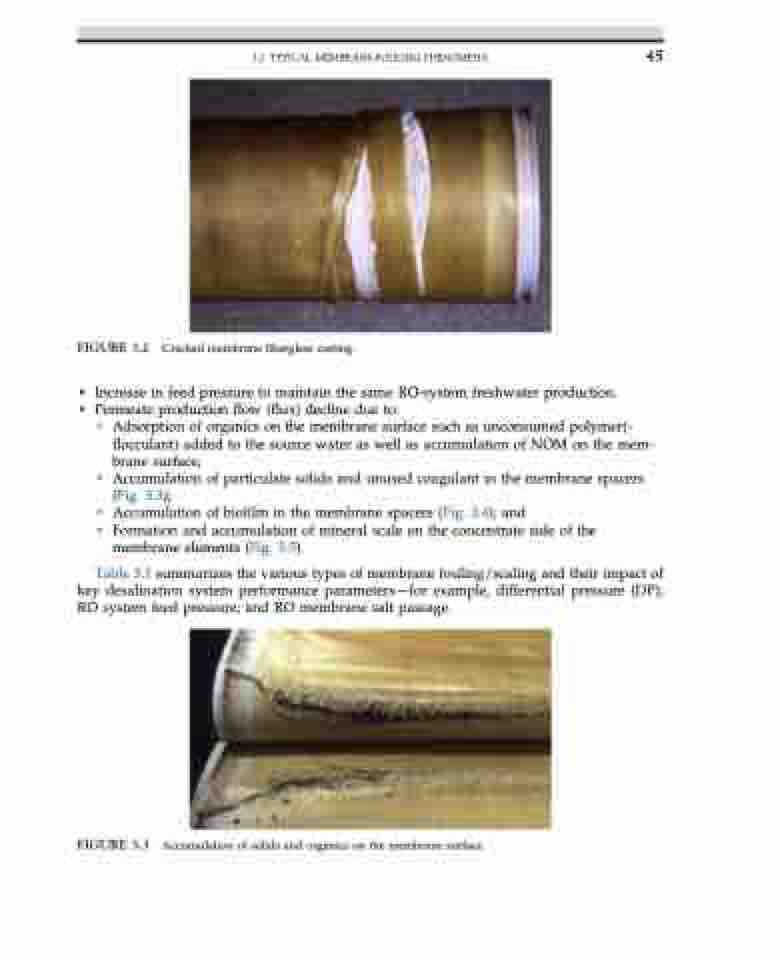
FIGURE 3.2 Cracked membrane fiberglass casting.
• Increase in feed pressure to maintain the same RO-system freshwater production. • Permeate production flow (flux) decline due to:
• Adsorption of organics on the membrane surface such as unconsumed polymer(- flocculant) added to the source water as well as accumulation of NOM on the mem- brane surface;
• Accumulation of particulate solids and unused coagulant in the membrane spacers (Fig. 3.3);
• Accumulation of biofilm in the membrane spacers (Fig. 3.4); and
• Formation and accumulation of mineral scale on the concentrate side of the
membrane elements (Fig. 3.5).
Table 3.1 summarizes the various types of membrane fouling/scaling and their impact of key desalination system performance parametersdfor example, differential pressure (DP); RO system feed pressure; and RO membrane salt passage.
FIGURE 3.3 Accumulation of solids and organics on the membrane surface.