Page 14 - C:\Users\r10sullivan\Documents\Flip PDF Professional\Bridgewater_Review_Nov_2018\
P. 14
daughter-in-law do all unpaid work Data shows that a daughter-in-law
with the latter doing disproportionately
more work. is the most time-poor individual
Data reveals surprising facts about the
effect of education on the division of in the multigenerational
labor in the household. In his pioneer- household as she undertakes
ing work on India, demographer John
Caldwell (1984) showed that universal significantly more total work,
education or mass schooling changed
the cultural superstructure of society. compared to all other members
He argued that educated women see
themselves as part of a larger world in the household.
and education acts to reduce “the hold
of the patriarch,” prepares children
of both genders to work in a market
economy, and informs girls of their mothers-in-law for a larger slice of the decrease her unpaid work and increase
economic options outside the home. family budget to spend on food, and her paid work in the economy.
Caldwell also argued that education health care for their children. Thus, According to Caldwell’s thesis, their
transformed the power relationship in a young daughter-in-law’s education paid work should increase, and un-
a multigenerational household such tips the traditional balance of famil- paid work should decrease as their
that, “a young woman with schooling ial relationships in her favor, and by education increases.
is more likely to challenge her in-laws, extension she is likely to exert more
and the in-laws are less likely to fight autonomy by doing less household Graph 2 shows the amount of work
the challenge” (412). According to work and demanding equal participa- done by daughters-in-law based on
him educated daughters-in-law can tion from her mother-in-law. Therefore their educational levels. Interestingly,
bargain successfully with less-educated one expects that an increase in the we see the exact opposite: as the educa-
education of a daughter-in-law would tion level of a daughter-in-law in a
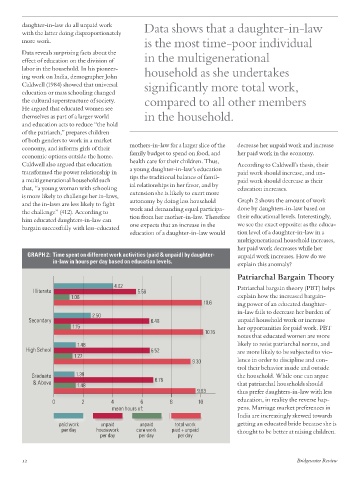
multigenerational household increases,
her paid work decreases while her
GRAPH 2: Time spent on different work activities (paid & unpaid) by daughter- unpaid work increases. How do we
in-law in hours per day based on education levels. explain this anomaly?
Patriarchal Bargain Theory
4.02 Patriarchal bargain theory (PBT) helps
Illiterate 5.58
1.06 explain how the increased bargain-
10.6 ing power of an educated daughter-
in-law fails to decrease her burden of
2.50
Secondary 6.48 unpaid household work or increase
1.15 her opportunities for paid work. PBT
10.16
notes that educated women are more
1.48 likely to resist patriarchal norms, and
High School 6.52 are more likely to be subjected to vio-
1.27
9.30 lence in order to discipline and con-
trol their behavior inside and outside
Graduate 1.39 the household. While one can argue
& Above 6.76 that patriarchal households should
1.48
9.63 thus prefer daughters-in-law with less
0 2 4 6 8 10 education, in reality the reverse hap-
mean hours of: pens. Marriage market preferences in
India are increasingly skewed towards
paid work unpaid unpaid total work getting an educated bride because she is
per day housework care work paid + unpaid thought to be better at raising children.
per day per day per day
12 Bridgewater Review