Page 79 - SAPEM-Chapter-10-2nd-edition-2014
P. 79
South African Pavement Engineering Manual
Chapter 10: Pavement Design
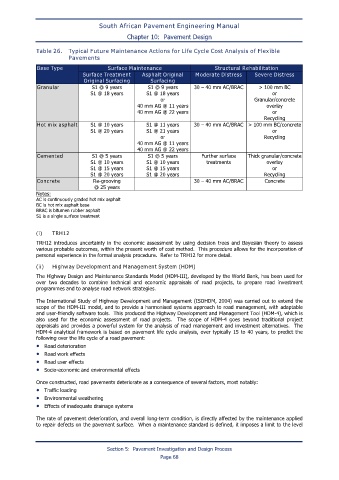
Table 26. Typical Future Maintenance Actions for Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Flexible
Pavements
Base Type Surface Maintenance Structural Rehabilitation
Surface Treatment Asphalt Original Moderate Distress Severe Distress
Original Surfacing Surfacing
Granular S1 @ 9 years S1 @ 9 years 30 – 40 mm AC/BRAC > 100 mm BC
S1 @ 18 years S1 @ 18 years or
or Granular/concrete
40 mm AG @ 11 years overlay
40 mm AG @ 22 years or
Recycling
Hot mix asphalt S1 @ 10 years S1 @ 11 years 30 – 40 mm AC/BRAC > 100 mm BC/concrete
S1 @ 20 years S1 @ 21 years or
or Recycling
40 mm AG @ 11 years
40 mm AG @ 22 years
Cemented S1 @ 5 years S1 @ 5 years Further surface Thick granular/concrete
S1 @ 10 years S1 @ 10 years treatments overlay
S1 @ 15 years S1 @ 15 years or
S1 @ 20 years S1 @ 20 years Recycling
Concrete Re-grooving 30 – 40 mm AC/BRAC Concrete
@ 25 years
Notes:
AC is continuously graded hot mix asphalt
BC is hot mix asphalt base
BRAC is bitumen rubber asphalt
S1 is a single surface treatment
(i) TRH12
TRH12 introduces uncertainty in the economic assessment by using decision trees and Bayesian theory to assess
various probable outcomes, within the present worth of cost method. This procedure allows for the incorporation of
personal experience in the formal analysis procedure. Refer to TRH12 for more detail.
(ii) Highway Development and Management System (HDM)
The Highway Design and Maintenance Standards Model (HDM-III), developed by the World Bank, has been used for
over two decades to combine technical and economic appraisals of road projects, to prepare road investment
programmes and to analyse road network strategies.
The International Study of Highway Development and Management (ISOHDM, 2004) was carried out to extend the
scope of the HDM-III model, and to provide a harmonised systems approach to road management, with adaptable
and user-friendly software tools. This produced the Highway Development and Management Tool (HDM-4), which is
also used for the economic assessment of road projects. The scope of HDM-4 goes beyond traditional project
appraisals and provides a powerful system for the analysis of road management and investment alternatives. The
HDM-4 analytical framework is based on pavement life cycle analysis, over typically 15 to 40 years, to predict the
following over the life cycle of a road pavement:
• Road deterioration
• Road work effects
• Road user effects
• Socio-economic and environmental effects
Once constructed, road pavements deteriorate as a consequence of several factors, most notably:
• Traffic loading
• Environmental weathering
• Effects of inadequate drainage systems
The rate of pavement deterioration, and overall long-term condition, is directly affected by the maintenance applied
to repair defects on the pavement surface. When a maintenance standard is defined, it imposes a limit to the level
Section 5: Pavement Investigation and Design Process
Page 68