Page 31 - Destination Risk and Resilience Manual-Namibia
P. 31
DESTINATION RISK AND RESILIENCE MANUAL
Peoples’ ability to act in the context of risk strongly tions is shaped by individual values, norms, and beliefs.
depends on their access to assets or capitals (human These factors serve both as enablers and barriers. Both
capital, social capital, natural capital, physical capital, enablers and barriers to pursuing resilient action will
and financial capital), while the willingness to take ac- be discussed in the following sections.
4.1 Enablers to destination resilience
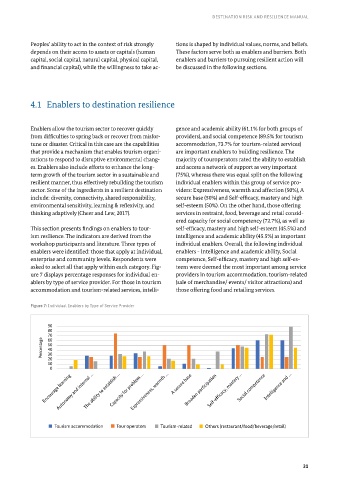
Enablers allow the tourism sector to recover quickly gence and academic ability (61.1% for both groups of
from difficulties to spring back or recover from misfor- providers), and social competence (89.5% for tourism
tune or disaster. Critical in this case are the capabilities accommodation, 73.7% for tourism-related services)
that provide a mechanism that enables tourism organi- are important enablers to building resilience. The
zations to respond to disruptive environmental chang- majority of touroperators rated the ability to establish
es. Enablers also include efforts to enhance the long- and access a network of support as very important
term growth of the tourism sector in a sustainable and (75%), whereas there was equal split on the following
resilient manner, thus effectively rebuilding the tourism individual enablers within this group of service pro-
sector. Some of the ingredients in a resilient destination viders: Expressiveness, warmth and affection (50%), A
include: diversity, connectivity, shared responsibility, secure base (50%) and Self-efficacy, mastery and high
environmental sensitivity, learning & reflexivity, and self-esteem (50%). On the other hand, those offering
thinking adaptively (Cheer and Lew, 2017). services in restraint, food, beverage and retail consid-
ered capacity for social competency (72.7%), as well as
This section presents findings on enablers to tour- self-efficacy, mastery and high self-esteem (45.5%) and
ism resilience. The indicators are derived from the intelligence and academic ability (45.5%) as important
workshop participants and literature. Three types of individual enablers. Overall, the following individual
enablers were identified: those that apply at individual, enablers - Intelligence and academic ability, Social
enterprise and community levels. Respondents were competence, Self-efficacy, mastery and high self-es-
asked to select all that apply within each category. Fig- teem were deemed the most important among service
ure 7 displays percentage responses for individual en- providers in tourism accommodation, tourism-related
ablers by type of service provider. For those in tourism (sale of merchandise/ events/ visitor attractions) and
accommodation and tourism-related services, intelli- those offering food and retailing services.
Figure 7: Individual Enablers by Type of Service Provider
90
80
70
60
Percentage 50
40
30
20
10
0
Self-ef
cacy, mastery …
Capacity for problem …
Autonomy and internal …
Encourage learning The ability to establish … Expressiveness, warmth … A secure base Broaden participation Social competence Intelligence and …
■ Tourism accommodation ■ Tour operators ■ Tourism-related ■ Others (restaurant/food/beverage/retail)
31