Page 3 - OK to Proceed - Ch 3 The Role of Digital Media in Medical Education
P. 3
Multimedia: Definition and Scope situations and problems. Both of these factors are
4
of paramount importance to the training clinician,
Multimedia, in its simplest form, is the presentation who must be able to not only draw from a multi-
of seen or heard words with accompanying pic- dimensional knowledge base, but also apply the
tures. Another definition describes multimedia as appropriate insights to clinical scenarios.
2
“an integration of multiple media elements (audio,
video, graphics, text, animation etc.) into one syn- Examples of Multimedia Applications
ergetic and symbiotic whole that results in more in Medicine
benefits for the end user than any one of the media
elements can provide individually.” Multimedia technology is utilized in a number of
3
This technology can be used not only in the settings across the medical landscape. Some of the
classroom setting, but across the medical landscape. most prominent are highlighted below.
From PowerPoint presentations and web-based
learning environments to simulation exercises and Telemedicine—Telemedicine refers to the provi-
interactive instructional videos, multimedia lies at sion of health care services by a remote provider
the heart of some of the most commonly used tools through telecommunication and information
and approaches in our profession. It is cost-effec- technologies. Individual technologies do not
5
tive, easily accessible, and flexible enough to target make up telecommunication as a whole; rather,
specific learning gaps. In addition, it has the power the term applies to the wider level of systems
to provide multiple representations of complex infor- and chain of care. Some common forms of
mation using mixed media forms. Because of these telemedicine include the reading of MRIs, X-rays,
advantages, many educational institutions have or CTs from distant sites (teleradiology); video
adopted multimedia instruction. consultations; remote surgery (telesurgery); and
The use of multimedia technology in instruction remote monitoring (electronic ICU). Since acces-
has proven particularly effective in promoting the sibility to health care is limited in many parts of
development of two important aspects of learn- the world, telemedicine, which relies heavily on
ing: retention, the ability to recall information, and multimedia technologies, serves an important
transfer, the application of learned concepts to new role in the fair and equal distribution of services.
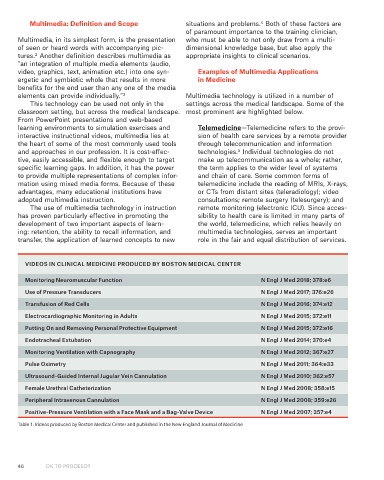
VIDEOS IN CLINICAL MEDICINE PRODUCED BY BOSTON MEDICAL CENTER
Monitoring Neuromuscular Function N Engl J Med 2018; 378:e6
Use of Pressure Transducers N Engl J Med 2017; 376:e26
Transfusion of Red Cells N Engl J Med 2016; 374:e12
Electrocardiographic Monitoring in Adults N Engl J Med 2015; 372:e11
Putting On and Removing Personal Protective Equipment N Engl J Med 2015; 372:e16
Endotracheal Extubation N Engl J Med 2014; 370:e4
Monitoring Ventilation with Capnography N Engl J Med 2012; 367:e27
Pulse Oximetry N Engl J Med 2011; 364:e33
Ultrasound-Guided Internal Jugular Vein Cannulation N Engl J Med 2010; 362:e57
Female Urethral Catheterization N Engl J Med 2008; 358:e15
Peripheral Intravenous Cannulation N Engl J Med 2008; 359:e26
Positive-Pressure Ventilation with a Face Mask and a Bag-Valve Device N Engl J Med 2007; 357:e4
Table 1. Videos produced by Boston Medical Center and published in the New England Journal of Medicine
46 OK TO PROCEED?