Page 13 - KG_1 Booklet - 2019
P. 13
Dovepress Evaluation of a tool for BGD in minimally invasive T-LIF
Volume of BG delivery T-LIF
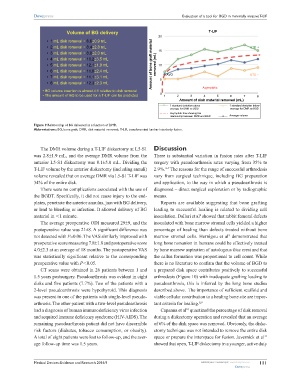
20
• 1 mL disk removal = 6.6±0.9 mL
• 2 mL disk removal = 8.4±2.8 mL STD +
• 3 mL disk removal = 8.8±2.0 mL 15
• 4 mL disk removal = 10.2±3.5 mL
• 5 mL disk removal = 12.1±1.9 mL Amount of bone graft material removed (mL) 10
• 6 mL disk removal = 11.6±2.4 mL
• 7 mL disk removal = 11.1±3.1 mL 5 AVG STD −
• 8 mL disk removal = 12.3±2.3 mL
• BG volume insertion is almost 4:1 relative to disk removal Asymptotic
• The amount of BG to be used for a T-LIF can be predicted 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Amount of disk material removed (mL)
1 standard deviation above 1 standard deviation below
average for DMR vs BGD average for DMR vs BGD
Asymptotic line showing the
relationship between DMR and BGD Average volume
Figure 9 Relationship of BG delivered as a function of DMR.
Abbreviations: BG, bone graft; DMR, disk material removed; T-LIF, transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion.
The DMR volume during a T-LIF diskectomy at L5-S1 Discussion
was 2.8±1.9 mL, and the average DMR volume from the There is substantial variation in fusion rates after T-LIF
anterior L5-S1 diskectomy was 8.1±5.0 mL. Dividing the surgery with pseudoarthrosis rates varying from 35% to
3–7
T-LIF volume by the anterior diskectomy (including annuli) 2.9%. The reasons for the range of successful arthrodesis
volume revealed that on average DMR via L5-S1 T-LIF was vary from surgical technique, including BG preparation
34% of the entire disk. and application, to the way in which a pseudoarthrosis is
There were no complications associated with the use of diagnosed – direct surgical exploration or by radiographic
the BGDT. Specifically, it did not cause injury to the end- means.
plates, penetrate the anterior annulus, jam with BG delivery, Reports are available suggesting that bone grafting
or lead to bleeding or infection. It allowed delivery of BG leading to successful healing is related to dividing cell
material in ,1 minute. inoculation. Dallari et al showed that rabbit femoral defects
8
The average preoperative ODI measured 29±9, and the inoculated with bone marrow stromal cells yielded a higher
postoperative value was 21±8. A significant difference was percentage of healing than defects treated without bone
9
not detected with P=0.06. The VAS similarly improved with marrow stromal cells. Hernigou et al demonstrated that
preoperative score measuring 7.8±1.8 and postoperative score long bone nonunion in humans could be effectively treated
4.0±2.3 at an average of 18 months. The postoperative VAS by bone marrow aspiration of autologous iliac crest and that
was statistically significant relative to the corresponding the callus formation was proportional to cell count. While
preoperative value with P,0.05. there is no literature to confirm that the volume of BGD to
CT scans were obtained in 26 patients between 1 and a prepared disk space contributes positively to successful
1.5 years postsurgery. Pseudoarthrosis was evident in eight arthrodesis (Figure 10) with inadequate grafting leading to
disks and five patients (7.7%). Two of the patients with a pseudoarthrosis, this is inferred by the long bone studies
2-level pseudoarthrosis were hypothyroid. This diagnosis described above. The importance of sufficient scaffold and
was present in one of the patients with single-level pseudo- viable cellular contribution to a healing bone site are impor-
arthrosis. The other patient with a two-level pseudoarthrosis tant criteria for healing. 8,9
10
had a diagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus infection Capanna et al quantized the percentage of disk removal
and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (HIV-AIDS). The during a diskectomy operation and revealed that an average
remaining pseudoarthrosis patient did not have discernible of 6% of the disk space was removed. Obviously, the diske-
risk factors (diabetes, tobacco consumption, or obesity). ctomy technique was not intended to remove the entire disk
A total of eight patients were lost to follow-up, and the aver- space or prepare the interspace for fusion. Javernick et al
11
age follow-up time was 1.5 years. showed that open, T-LIF diskectomy in a younger, active duty
Medical Devices: Evidence and Research 2016:9 submit your manuscript | www.dovepress.com 111
Dovepress