Page 5 - revision
P. 5
Orouba Language Schools Third Preparatory
Computer Department Second Term 2017/2018
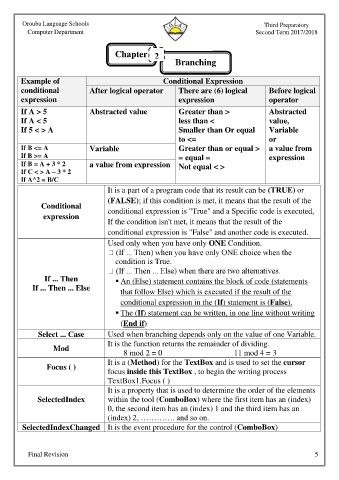
Chapter 2 Branching
Example of Conditional Expression Before logical
conditional After logical operator There are (6) logical operator
expression
If A > 5 expression Abstracted
If A < 5 value,
If 5 < > A Abstracted value Greater than > Variable
less than < or
If B <= A Variable Smaller than Or equal a value from
If B >= A a value from expression to <= expression
If B = A + 3 * 2 Greater than or equal >
If C < > A – 3 * 2 = equal =
If A^2 = B/C Not equal < >
Conditional It is a part of a program code that its result can be (TRUE) or
expression (FALSE); if this condition is met, it means that the result of the
conditional expression is "True" and a Specific code is executed,
If the condition isn't met, it means that the result of the
conditional expression is "False" and another code is executed.
Used only when you have only ONE Condition.
condition is True.
If ... Then An (Else) statement contains the block of code (statements
If ... Then ... Else
that follow Else) which is executed if the result of the
Select ... Case
Mod conditional expression in the (If) statement is (False).
Focus ( ) The (If) statement can be written, in one line without writing
SelectedIndex (End if)
SelectedIndexChanged
Used when branching depends only on the value of one Variable.
It is the function returns the remainder of dividing.
8 mod 2 = 0 11 mod 4 = 3
It is a (Method) for the TextBox and is used to set the cursor
focus inside this TextBox , to begin the writing process
TextBox1.Focus ( )
It is a property that is used to determine the order of the elements
within the tool (ComboBox) where the first item has an (index)
0, the second item has an (index) 1 and the third item has an
(index) 2, …………. and so on.
It is the event procedure for the control (ComboBox)
Final Revision 5