Page 280 - Pharmacology Mnemonics and Short Notes
P. 280
272
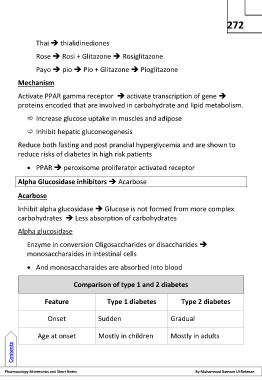
Thai thialidinediones
Rose Rosi + Glitazone Rosiglitazone
Payo pio Pio + Glitazone Pioglitazone
Mechanism
Activate PPAR gamma receptor activate transcription of gene
proteins encoded that are involved in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Increase glucose uptake in muscles and adipose
Inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis
Reduce both fasting and post prandial hyperglycemia and are shown to
reduce risks of diabetes in high risk patients
PPAR peroxisome proliferator activated receptor
Alpha Glucosidase inhibitors Acarbose
Acarbose
Inhibit alpha glucosidase Glucose is not formed from more complex
carbohydrates Less absorption of carbohydrates
Alpha glucosidase
Enzyme in conversion Oligosaccharides or disaccharides
monosaccharaides in intestinal cells
And monosaccharaides are absorbed into blood
Comparison of type 1 and 2 diabetes
Feature Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes
Onset Sudden Gradual
Age at onset Mostly in children Mostly in adults
Contents
Pharmacology Mnemonics and Short Notes By Muhammad Ramzan Ul Rehman