Page 10 - AIU Distance Learning Courses - Sample
P. 10
of the earth. Yet your brain with its hundred thousand billion electrical connections fits in a quart jar
and operates for 70 years on ten watts of power, fueled largely by cheeseburgers and French fries.
Every cubic inch [2.54 centimeters] of the human brain contains at least 100 million nerve cells
interconnected by 10 thousand miles of fibers.
It has been said that man's 3-4-pound brain is the most complex and orderly arrangement of matter in
2
the entire universe! Far more complicated than any computer, the human brain is capable of storing
and creatively manipulating seemingly infinite amounts of information. Its capabilities and potential
stagger the imagination. The more we use it, the better it becomes.
The brain capabilities of even the smallest insects are mind-boggling. The tiny speck of a brain found in
a little ant, butterfly or bee enable them not only to see, smell, taste and move, but even to fly with
great precision. Butterflies routinely navigate enormous distances. Bees and ants carry on complex
social organizations, building projects, and communications. These miniature brains put our computers
and avionics to shame, in comparison.
The eye...can distinguish among seven million colors. It has automatic
focusing and handles an astounding 1.5 million messages --
3
simultaneously. Evolution focuses on mutations and changes from and
within existing organisms. Yet evolution alone cannot explain the initial
source of the eye or the brain.
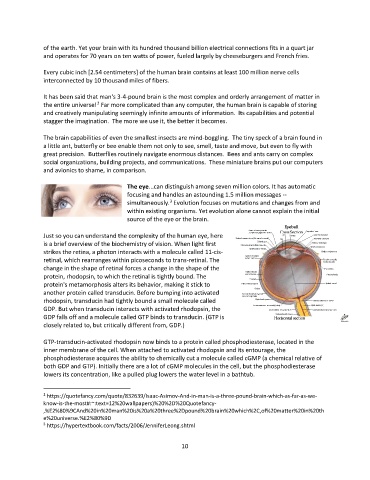
Just so you can understand the complexity of the human eye, here
is a brief overview of the biochemistry of vision. When light first
strikes the retina, a photon interacts with a molecule called 11-cis-
retinal, which rearranges within picoseconds to trans-retinal. The
change in the shape of retinal forces a change in the shape of the
protein, rhodopsin, to which the retinal is tightly bound. The
protein's metamorphosis alters its behavior, making it stick to
another protein called transducin. Before bumping into activated
rhodopsin, transducin had tightly bound a small molecule called
GDP. But when transducin interacts with activated rhodopsin, the
GDP falls off and a molecule called GTP binds to transducin. (GTP is
closely related to, but critically different from, GDP.)
GTP-transducin-activated rhodopsin now binds to a protein called phosphodiesterase, located in the
inner membrane of the cell. When attached to activated rhodopsin and its entourage, the
phosphodiesterase acquires the ability to chemically cut a molecule called cGMP (a chemical relative of
both GDP and GTP). Initially there are a lot of cGMP molecules in the cell, but the phosphodiesterase
lowers its concentration, like a pulled plug lowers the water level in a bathtub.
2 https://quotefancy.com/quote/832639/Isaac-Asimov-And-in-man-is-a-three-pound-brain-which-as-far-as-we-
know-is-the-most#:~:text=12%20wallpapers)%20%2D%20Quotefancy-
,%E2%80%9CAnd%20in%20man%20is%20a%20three%2Dpound%20brain%20which%2C,of%20matter%20in%20th
e%20universe.%E2%80%9D
3 https://hypertextbook.com/facts/2006/JenniferLeong.shtml
10