Page 189 - A Canuck's Guide to Financial Literacy 2020
P. 189
189
Exchange Traded Funds
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) are an investment solution structured similar to a mutual
fund that are listed on the stock market. These ETFs are attractive to investors due to their
low cost, tax efficiency and stock like features. ETFs are able to invest in various asset
classes such as stocks, bonds, currencies, commodities and more. One of the most popular
ETFs is the SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) that tracks the S&P 500 index.
ETF Construction
ETFs have many similarities to stocks as they’re bought and sold the same way on an
exchange. As an EF is a basket of stocks, they offer much more diversification than
purchasing an individual stock. This is one of the unique advantages of ETFs which makes
them so popular. Why expose yourself to additional risk when buying a single stock when
you can purchase an entire market sector, index or foreign market?
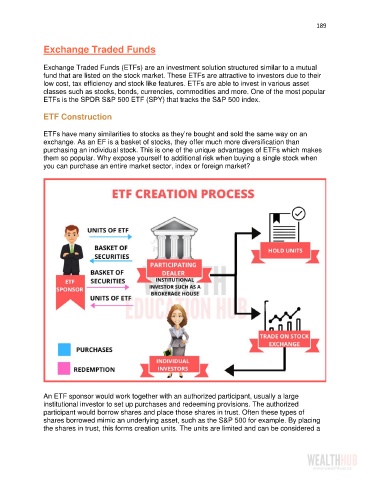
An ETF sponsor would work together with an authorized participant, usually a large
institutional investor to set up purchases and redeeming provisions. The authorized
participant would borrow shares and place those shares in trust. Often these types of
shares borrowed mimic an underlying asset, such as the S&P 500 for example. By placing
the shares in trust, this forms creation units. The units are limited and can be considered a