Page 197 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 197
P1: KPE
BLUK007-05 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 8:52 Char Count= 0
Chapter 5: Disorders of the liver 193
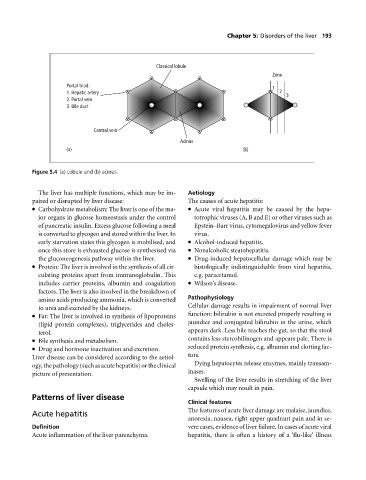
Classical lobule
Zone
Portal triad: 1
1. Hepatic artery 2 3
2. Portal vein
3. Bile duct
Central vein
Acinus
(a) (b)
Figure 5.4 (a) Lobule and (b) acinus.
The liver has multiple functions, which may be im- Aetiology
paired or disrupted by liver disease: The causes of acute hepatitis:
Carbohydrate metabolism: The liver is one of the ma- Acute viral hepatitis may be caused by the hepa-
jor organs in glucose homeostasis under the control totrophic viruses (A, B and E) or other viruses such as
of pancreatic insulin. Excess glucose following a meal Epstein–Barr virus, cytomegalovirus and yellow fever
is converted to glycogen and stored within the liver. In virus.
early starvation states this glycogen is mobilised, and Alcohol-induced hepatitis.
once this store is exhausted glucose is synthesised via Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
the gluconeogenesis pathway within the liver. Drug-induced hepatocellular damage which may be
Protein: The liver is involved in the synthesis of all cir- histologically indistinguishable from viral hepatitis,
culating proteins apart from immunoglobulin. This e.g. paracetamol.
includes carrier proteins, albumin and coagulation Wilson’s disease.
factors. The liver is also involved in the breakdown of
amino acids producing ammonia, which is converted Pathophysiology
to urea and excreted by the kidneys. Cellular damage results in impairment of normal liver
Fat: The liver is involved in synthesis of lipoproteins
function: bilirubin is not excreted properly resulting in
(lipid protein complexes), triglycerides and choles- jaundice and conjugated bilirubin in the urine, which
terol. appears dark. Less bile reaches the gut, so that the stool
Bile synthesis and metabolism.
contains less stercobilinogen and appears pale. There is
Drug and hormone inactivation and excretion.
reduced protein synthesis, e.g. albumin and clotting fac-
Liver disease can be considered according to the aetiol- tors.
ogy,thepathology(suchasacutehepatitis)ortheclinical Dying hepatocytes release enzymes, mainly transam-
picture of presentation. inases.
Swelling of the liver results in stretching of the liver
capsule which may result in pain.
Patterns of liver disease
Clinical features
The features of acute liver damage are malaise, jaundice,
Acute hepatitis
anorexia, nausea, right upper quadrant pain and in se-
Definition vere cases, evidence of liver failure. In cases of acute viral
Acute inflammation of the liver parenchyma. hepatitis, there is often a history of a ‘flu-like’ illness