Page 202 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 202
P1: KPE
BLUK007-05 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 8:52 Char Count= 0
198 Chapter 5: Hepatic, biliary and pancreatic systems
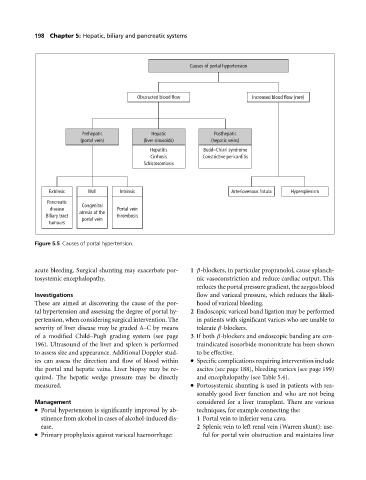
Causes of portal hypertension
Obstructed blood flow Increased blood flow (rare)
Prehepatic Hepatic Posthepatic
(portal vein) (liver sinusoids) (hepatic veins)
Hepatitis Budd–Chiari syndrome
Cirrhosis Constrictive pericarditis
Schistosomiasis
Extrinsic Wall Intrinsic Arteriovenous fistula Hypersplenism
Pancreatic Congenital
disease Portal vein
Biliary tract atresia of the thrombosis
portal vein
tumours
Figure 5.5 Causes of portal hypertension.
acute bleeding. Surgical shunting may exacerbate por- 1 β-blockers, in particular propranolol, cause splanch-
tosystemic encephalopathy. nic vasoconstriction and reduce cardiac output. This
reduces the portal pressure gradient, the azygos blood
Investigations flow and variceal pressure, which reduces the likeli-
These are aimed at discovering the cause of the por- hood of variceal bleeding.
tal hypertension and assessing the degree of portal hy- 2 Endoscopic variceal band ligation may be performed
pertension, when considering surgical intervention. The in patients with significant varices who are unable to
severity of liver disease may be graded A–C by means tolerate β-blockers.
of a modified Child–Pugh grading system (see page 3 If both β-blockers and endoscopic banding are con-
196). Ultrasound of the liver and spleen is performed traindicated isosorbide mononitrate has been shown
to assess size and appearance. Additional Doppler stud- to be effective.
ies can assess the direction and flow of blood within Specific complications requiring intervention include
the portal and hepatic veins. Liver biopsy may be re- ascites (see page 188), bleeding varices (see page 199)
quired. The hepatic wedge pressure may be directly and encephalopathy (see Table 5.4).
measured. Portosystemic shunting is used in patients with rea-
sonably good liver function and who are not being
Management considered for a liver transplant. There are various
Portal hypertension is significantly improved by ab- techniques, for example connecting the:
stinence from alcohol in cases of alcohol-induced dis- 1 Portal vein to inferior vena cava.
ease. 2 Splenic vein to left renal vein (Warren shunt): use-
Primary prophylaxis against variceal haemorrhage: ful for portal vein obstruction and maintains liver