Page 205 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 205
P1: KPE
BLUK007-05 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 8:52 Char Count= 0
Chapter 5: Disorders of the liver 201
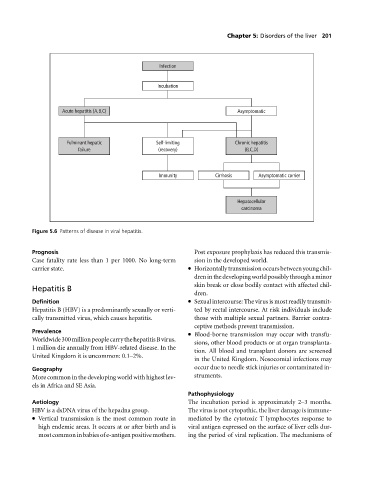
Infection
Incubation
Acute hepatitis (A,B,C) Asymptomatic
Fulminant hepatic Self-limiting Chronic hepatitis
failure (recovery) (B,C,D)
Immunity Cirrhosis Asymptomatic carrier
Hepatocellular
carcinoma
Figure 5.6 Patterns of disease in viral hepatitis.
Prognosis Post exposure prophylaxis has reduced this transmis-
Case fatality rate less than 1 per 1000. No long-term sion in the developed world.
carrier state. Horizontallytransmissionoccursbetweenyoungchil-
dreninthedevelopingworldpossiblythroughaminor
skin break or close bodily contact with affected chil-
Hepatitis B
dren.
Definition Sexual intercourse: The virus is most readily transmit-
Hepatitis B (HBV) is a predominantly sexually or verti- tedbyrectal intercourse. At risk individuals include
cally transmitted virus, which causes hepatitis. those with multiple sexual partners. Barrier contra-
ceptive methods prevent transmission.
Prevalence Blood-borne transmission may occur with transfu-
Worldwide300millionpeoplecarrythehepatitisBvirus,
sions, other blood products or at organ transplanta-
1 million die annually from HBV-related disease. In the
tion. All blood and transplant donors are screened
United Kingdom it is uncommon: 0.1–2%.
in the United Kingdom. Nosocomial infections may
Geography occur due to needle stick injuries or contaminated in-
More common in the developing world with highest lev- struments.
els in Africa and SE Asia.
Pathophysiology
Aetiology The incubation period is approximately 2–3 months.
HBV is a dsDNA virus of the hepadna group. The virus is not cytopathic, the liver damage is immune-
Vertical transmission is the most common route in mediated by the cytotoxic T lymphocytes response to
high endemic areas. It occurs at or after birth and is viral antigen expressed on the surface of liver cells dur-
mostcommoninbabiesofe-antigenpositivemothers. ing the period of viral replication. The mechanisms of