Page 207 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 207
P1: KPE
BLUK007-05 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 8:52 Char Count= 0
Chapter 5: Disorders of the liver 203
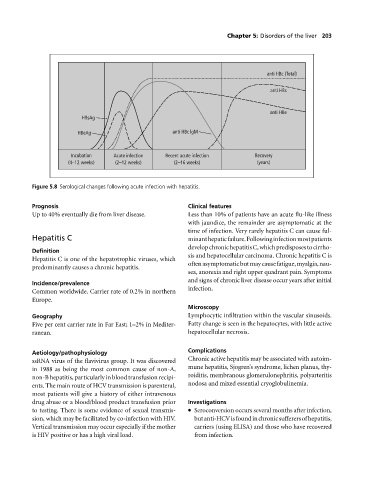
anti HBc (Total)
anti HBs
anti HBe
HBsAg
HBeAg anti HBc lgM
Incubation Acute infection Recent acute infection Recovery
(4–12 weeks) (2–12 weeks) (2–16 weeks) (years)
Figure 5.8 Serological changes following acute infection with hepatitis.
Prognosis Clinical features
Up to 40% eventually die from liver disease. Less than 10% of patients have an acute flu-like illness
with jaundice, the remainder are asymptomatic at the
time of infection. Very rarely hepatitis C can cause ful-
Hepatitis C minanthepaticfailure.Followinginfectionmostpatients
developchronichepatitisC,whichpredisposestocirrho-
Definition
sis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Chronic hepatitis C is
Hepatitis C is one of the hepatotrophic viruses, which
oftenasymptomaticbutmaycausefatigue,myalgia,nau-
predominantly causes a chronic hepatitis.
sea, anorexia and right upper quadrant pain. Symptoms
and signs of chronic liver disease occur years after initial
Incidence/prevalence
infection.
Common worldwide. Carrier rate of 0.2% in northern
Europe.
Microscopy
Geography Lymphocytic infiltration within the vascular sinusoids.
Five per cent carrier rate in Far East; 1–2% in Mediter- Fatty change is seen in the hepatocytes, with little active
ranean. hepatocellular necrosis.
Complications
Aetiology/pathophysiology
ssRNA virus of the flavivirus group. It was discovered Chronic active hepatitis may be associated with autoim-
in 1988 as being the most common cause of non-A, mune hepatitis, Sjogren’s syndrome, lichen planus, thy-
non-B hepatitis, particularly in blood transfusion recipi- roiditis, membranous glomerulonephritis, polyarteritis
ents. The main route of HCV transmission is parenteral, nodosa and mixed essential cryoglobulinemia.
most patients will give a history of either intravenous
drug abuse or a blood/blood product transfusion prior Investigations
to testing. There is some evidence of sexual transmis- Seroconversion occurs several months after infection,
sion, which may be facilitated by co-infection with HIV. butanti-HCVisfoundinchronicsufferersofhepatitis,
Vertical transmission may occur especially if the mother carriers (using ELISA) and those who have recovered
is HIV positive or has a high viral load. from infection.