Page 211 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 211
P1: KPE
BLUK007-05 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 8:52 Char Count= 0
Chapter 5: Disorders of the liver 207
Clinical features Drug-induced liver disease
Most patients are asymptomatic, fatigue, malaise and
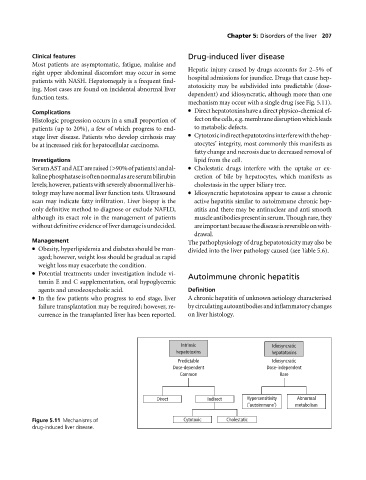
Hepatic injury caused by drugs accounts for 2–5% of
rightupper abdominal discomfort may occur in some
hospital admissions for jaundice. Drugs that cause hep-
patients with NASH. Hepatomegaly is a frequent find-
atotoxicity may be subdivided into predictable (dose-
ing. Most cases are found on incidental abnormal liver
dependent) and idiosyncratic, although more than one
function tests.
mechanism may occur with a single drug (see Fig. 5.11).
Complications Direct hepatotoxins have a direct physico-chemical ef-
Histologic progression occurs in a small proportion of fectonthecells,e.g.membranedisruptionwhichleads
patients (up to 20%), a few of which progress to end- to metabolic defects.
stage liver disease. Patients who develop cirrhosis may Cytotoxicindirecthepatotoxinsinterferewiththehep-
be at increased risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. atocytes’ integrity, most commonly this manifests as
fatty change and necrosis due to decreased removal of
Investigations lipid from the cell.
SerumASTandALTareraised(>90%ofpatients)andal- Cholestatic drugs interfere with the uptake or ex-
kalinephosphataseisoftennormalasareserumbilirubin cretion of bile by hepatocytes, which manifests as
levels;however,patientswithseverelyabnormalliverhis- cholestasis in the upper biliary tree.
tology may have normal liver function tests. Ultrasound Idiosyncratic hepatotoxins appear to cause a chronic
scan may indicate fatty infiltration. Liver biopsy is the active hepatitis similar to autoimmune chronic hep-
only definitive method to diagnose or exclude NAFLD, atitis and there may be antinuclear and anti smooth
although its exact role in the management of patients muscleantibodiespresentinserum.Thoughrare,they
withoutdefinitiveevidenceofliverdamageisundecided. areimportantbecausethediseaseisreversibleonwith-
drawal.
Management The pathophysiology of drug hepatotoxicity may also be
Obesity, hyperlipidemia and diabetes should be man- divided into the liver pathology caused (see Table 5.6).
aged; however, weight loss should be gradual as rapid
weight loss may exacerbate the condition.
Potential treatments under investigation include vi- Autoimmune chronic hepatitis
tamin E and C supplementation, oral hypoglycemic
agents and ursodeoxycholic acid. Definition
In the few patients who progress to end stage, liver
Achronic hepatitis of unknown aetiology characterised
failure transplantation may be required; however, re- bycirculatingautoantibodiesandinflammatorychanges
currence in the transplanted liver has been reported. on liver histology.
Intrinsic Idiosyncratic
hepatotoxins hepatotoxins
Predictable Idiosyncratic
Dose-dependent Dose-independent
Common Rare
Direct Indirect Hypersensitivity Abnormal
(‘autoimmune’) metabolism
Figure 5.11 Mechanisms of Cytotoxic Cholestatic
drug-induced liver disease.