Page 220 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 220
P1: KPE
BLUK007-05 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 8:52 Char Count= 0
216 Chapter 5: Hepatic, biliary and pancreatic systems
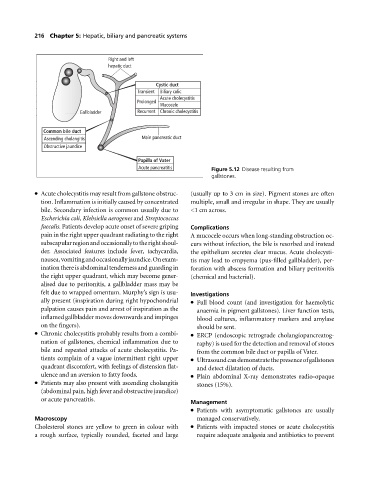
Right and left
hepatic duct
Cystic duct
Transient Biliary colic
Acute cholecystitis
Prolonged
Mucocele
Gallbladder Recurrent Chronic cholecystitis
Common bile duct
Ascending cholangitis Main pancreatic duct
Obstructive jaundice
Papilla of Vater
Acute pancreatitis Figure 5.12 Disease resulting from
gallstones.
Acute cholecystitis may result from gallstone obstruc- (usually up to 3 cm in size). Pigment stones are often
tion. Inflammation is initially caused by concentrated multiple, small and irregular in shape. They are usually
bile. Secondary infection is common usually due to <1 cm across.
Escherichia coli, Klebsiella aerogenes and Streptococcus
faecalis.Patients develop acute onset of severe griping Complications
pain in the right upper quadrant radiating to the right Amucocele occurs when long-standing obstruction oc-
subscapularregionandoccasionallytotherightshoul- curs without infection, the bile is resorbed and instead
der. Associated features include fever, tachycardia, the epithelium secretes clear mucus. Acute cholecysti-
nausea,vomitingandoccasionallyjaundice.Onexam- tis may lead to empyema (pus-filled gallbladder), per-
ination there is abdominal tenderness and guarding in foration with abscess formation and biliary peritonitis
the right upper quadrant, which may become gener- (chemical and bacterial).
alised due to peritonitis, a gallbladder mass may be
felt due to wrapped omentum. Murphy’s sign is usu- Investigations
ally present (inspiration during right hypochondrial Full blood count (and investigation for haemolytic
palpation causes pain and arrest of inspiration as the anaemia in pigment gallstones). Liver function tests,
inflamed gallbladder moves downwards and impinges blood cultures, inflammatory markers and amylase
on the fingers). should be sent.
Chronic cholecystitis probably results from a combi- ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatog-
nation of gallstones, chemical inflammation due to raphy) is used for the detection and removal of stones
bile and repeated attacks of acute cholecystitis. Pa- from the common bile duct or papilla of Vater.
tients complain of a vague intermittent right upper Ultrasoundcandemonstratethepresenceofgallstones
quadrant discomfort, with feelings of distension flat- and detect dilatation of ducts.
ulence and an aversion to fatty foods. Plain abdominal X-ray demonstrates radio-opaque
Patients may also present with ascending cholangitis stones (15%).
(abdominal pain, high fever and obstructive jaundice)
or acute pancreatitis.
Management
Patients with asymptomatic gallstones are usually
Macroscopy managed conservatively.
Cholesterol stones are yellow to green in colour with Patients with impacted stones or acute cholecystitis
arough surface, typically rounded, faceted and large require adequate analgesia and antibiotics to prevent