Page 339 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 339
P1: FAW
BLUK007-07 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 18:18 Char Count= 0
Chapter 7: Disorders of cranial and peripheral nerves 335
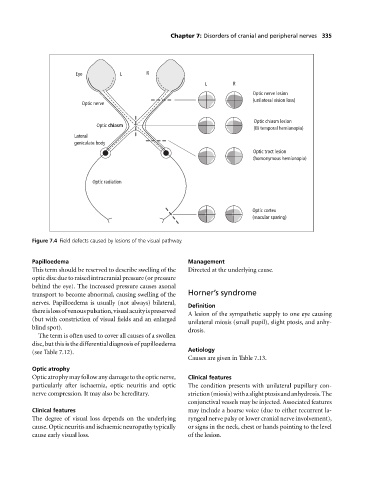
Eye L R
L R
Optic nerve lesion
(unilateral vision loss)
Optic nerve
Optic chiasm lesion
Optic chiasm
(Bi temporal hemianopia)
Lateral
geniculate body
Optic tract lesion
(homonymous hemianopia)
Optic radiation
Optic cortex
(macular sparing)
Figure 7.4 Field defects caused by lesions of the visual pathway.
Papilloedema Management
This term should be reserved to describe swelling of the Directed at the underlying cause.
optic disc due to raised intracranial pressure (or pressure
behind the eye). The increased pressure causes axonal
transport to become abnormal, causing swelling of the Horner’s syndrome
nerves. Papilloedema is usually (not always) bilateral,
Definition
thereislossofvenouspulsation,visualacuityispreserved
A lesion of the sympathetic supply to one eye causing
(but with constriction of visual fields and an enlarged
unilateral miosis (small pupil), slight ptosis, and anhy-
blind spot).
drosis.
The term is often used to cover all causes of a swollen
disc, but this is the differential diagnosis of papilloedema
(see Table 7.12). Aetiology
Causes are given in Table 7.13.
Optic atrophy
Optic atrophy may follow any damage to the optic nerve, Clinical features
particularly after ischaemia, optic neuritis and optic The condition presents with unilateral pupillary con-
nerve compression. It may also be hereditary. striction(miosis)withaslightptosisandanhydrosis.The
conjunctival vessels may be injected. Associated features
Clinical features may include a hoarse voice (due to either recurrent la-
The degree of visual loss depends on the underlying ryngeal nerve palsy or lower cranial nerve involvement),
cause. Optic neuritis and ischaemic neuropathy typically or signs in the neck, chest or hands pointing to the level
cause early visual loss. of the lesion.